Accelerate Your Smart Factory Initiatives Using a Next-Generation MES
Don’t let a legacy manufacturing execution system (MES) hold you back.
Speak With A Representative
Request Content Access
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.
- You lack real-time visibility into production processes, machine performance, and product quality.
- Your existing MES platform is operating in data silos without integration with other critical enterprise systems.
- Your legacy MES cannot handle flexibility and scalability needed to manage multisite operations.
- You lack predictive maintenance features, resulting in frequent and expensive downtimes.
- You struggle to comply with modern regulatory standards or support sustainability initiatives due to lack of real-time monitoring and reporting features.
Our Advice
Critical Insight
CIOs can transform MES from a cost center into a competitive advantage creator by choosing a best-fit product that can integrate well with enterprise software and is capable of leveraging AI, IIOT, and cloud infrastructure.
Impact and Result
Info-Tech recognizes the role of CIOs in enabling smart factory and digitalization initiatives. This research aims to empower CIOs with the knowledge and tools necessary to evaluate and implement next-gen MES platforms to ensure their respective organizations remain competitive.
Info-Tech will provide:
- A comprehensive guide explaining the benefits of next-gen MES platforms and a buyers guide to help CIOs evaluate, compare, and eventually choose the best-fit MES solution.
- A deployment readiness tool to help CIOs assess their organizational readiness to implement a next gen MES.
Accelerate Your Smart Factory Initiatives Using a Next-Generation MES Research & Tools
1. Accelerate Your Smart Factory Initiatives Using a Next-Generation MES Storyboard – Research that aims to empower CIOs with the knowledge and tools necessary to evaluate and implement next-gen MES platforms to ensure their organizations remain competitive.
As manufacturing has become more complex and global, legacy monolithic systems are failing to keep pace with the need for connectivity, real-time visibility, and advanced analytics. The shift toward a next-generation, cloud-native MES platform is essential for companies aiming to achieve Industry 4.0 maturity.
2. Next-Gen MES Deployment Readiness Tool – A tool that helps CIOs get clarity on organizational readiness, prioritize efforts, allocate resources effectively, and make informed decisions for a successful MES implementation.
By guiding users through a structured evaluation across key dimensions of preparedness, this tool provides actionable insights into the organization’s current readiness to implement a next-generation, cloud-native MES and identifies areas requiring improvement to ensure a smooth and effective deployment.
Speak With A Representative
Request Content Access
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.
Accelerate Your Smart Factory Initiatives Using a Next-Generation MES
Don’t let a legacy manufacturing execution system (MES) hold you back.
Analyst perspective
Don’t let a legacy MES hold you back.
Manufacturing execution systems (MES), once the foundation of shop floor control, are increasingly considered expensive, rigid, and outdated. Legacy monolithic MES systems lack the flexibility to scale with modern manufacturing needs and are becoming a barrier to embracing Industry 4.0 technologies. As manufacturing has become more complex and global, these systems are failing to keep pace with the need for connectivity, real-time visibility, and advanced analytics.
The shift toward a next-generation, cloud-native MES platform is essential for companies aiming to achieve Industry 4.0 maturity. A next-generation MES incorporates Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), cloud computing, and artificial intelligence (AI) to offer manufacturers real-time insights, predictive maintenance, and production optimization across multiple sites. By leveraging advanced technologies, manufacturers can streamline operations, reduce downtime, and enhance product quality thus responding quickly to market changes. The ability to connect machines, sensors, and systems across the enterprise in real time allows for greater coordination and process optimization.
Additionally, next-generation MES supports sustainability initiatives and regulatory compliance, providing real-time data on resource consumption, waste, and emissions. Legacy MES systems often lack the necessary integration to track these metrics, putting companies at risk of falling behind competitors that have adopted more advanced, data-driven approaches to sustainability.
As the manufacturing industry moves toward smarter, more connected operations, CIOs must prioritize the adoption of next-generation MES to unlock new levels of efficiency, agility, and growth to remain competitive.

Shreyas Shukla
Principal Research Director, Industry
Info-Tech Research Group
Executive summary
|
Your Challenge |
Common Obstacles |
Info-Tech’s Approach |
|---|---|---|
|
You lack real-time visibility into production processes, machine performance, and product quality. Your existing MES platform is operating in data silos without integration with other, critical enterprise systems. Your legacy MES cannot handle the flexibility and scalability needed to manage multi-site operations. You lack predictive maintenance features resulting in frequent and expensive downtimes. You struggle to comply with modern regulatory standards or support sustainability initiatives due to lack of real-time monitoring and reporting features. |
Significant upfront capital is required for MES implementation and related software, hardware, and infrastructure upgrades. Integrating new MES with existing legacy systems and custom-built software can be complex, time-consuming, and costly. Implementing a next-gen MES requires significant changes to established processes, workflows, and employee roles. Lack of specialized skills in data analytics, IT, and operations management. Concerns about data security, regulatory compliance, and loss of control over sensitive production data when moving to a cloud-based/hybrid MES solution. |
Info-Tech recognizes the role of CIOs in enabling smart factory and digitalization initiatives. This research aims to empower CIOs with the knowledge and tools necessary to evaluate and implement next-gen MES platforms to ensure their organizations remain competitive. Info-Tech will provide:
|
CIOs can transform MES from a cost center to a competitive advantage creator by choosing a best-fit product that can integrate well with enterprise software and is capable of leveraging AI, IIoT, and cloud infrastructure.
Manufacturers understand that transformation is critical
Manufacturers face continuing uncertainty and changing market conditions. Organizations realize that digital transformation is essential before challenges become difficult to address.
Less than 30% of all transformation efforts have been successful over the last three decades.
19951
20052
20103
20154
20215
Sources: 1 - Harvard Business Review, 1995 2 - Wiley Online Library, 2007 3 - Harvard Business Press, 2010 4 - McKinsey & Company, 2015 5 - McKinsey & Company, 2021
Manufacturers have seen limited success in achieving their ambitious transformation objectives.
25% successful
25% failed
50% partially successful
Source: Oliver Wyman, 2023
Manufacturers are allocating funds for large-scale transformation efforts.
“100% of companies made transformation efforts within the last three years.”
On average, manufacturers are spending between $1.5 to $2 to achieve $1 of run-rate benefit from transformation efforts.
Source: Oliver Wyman, 2023
Data is at the center of a successful transformation
Manufacturing organizations generate data across corporate processes and in their factories, warehouses and other nodes of the supply chain network. Transformation and daily operations rely on digital data, analysis, and its use in effective decision-making across all levels of the organization.
Embedding insights from data into business strategy is crucial for your success.
1995 – IT is a support function
2005 – Data not part of business strategy
2010 – Data strategy aligned with business strategy
2015 – Data-inspired business strategies emerge
2021 – Data-driven business strategies become the norm
Sources: Jeff Winter Insights, 2024; Zscaler, 2024
“In fact, 91% of surveyed manufacturing executives consider data sharing to be at least somewhat important.”
Source: World Economic Forum, 2021
Understanding how to use data from the top floor and the shop floor is critical for modern manufacturing.

Info-Tech Insight
Application platforms such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) and MES are key in enabling effective data collection and data-driven insights which manufacturers can use to inform their transformation efforts and adjust their production to respond to market conditions in line with their own objectives.
Manufacturers are frustrated with traditional MES systems
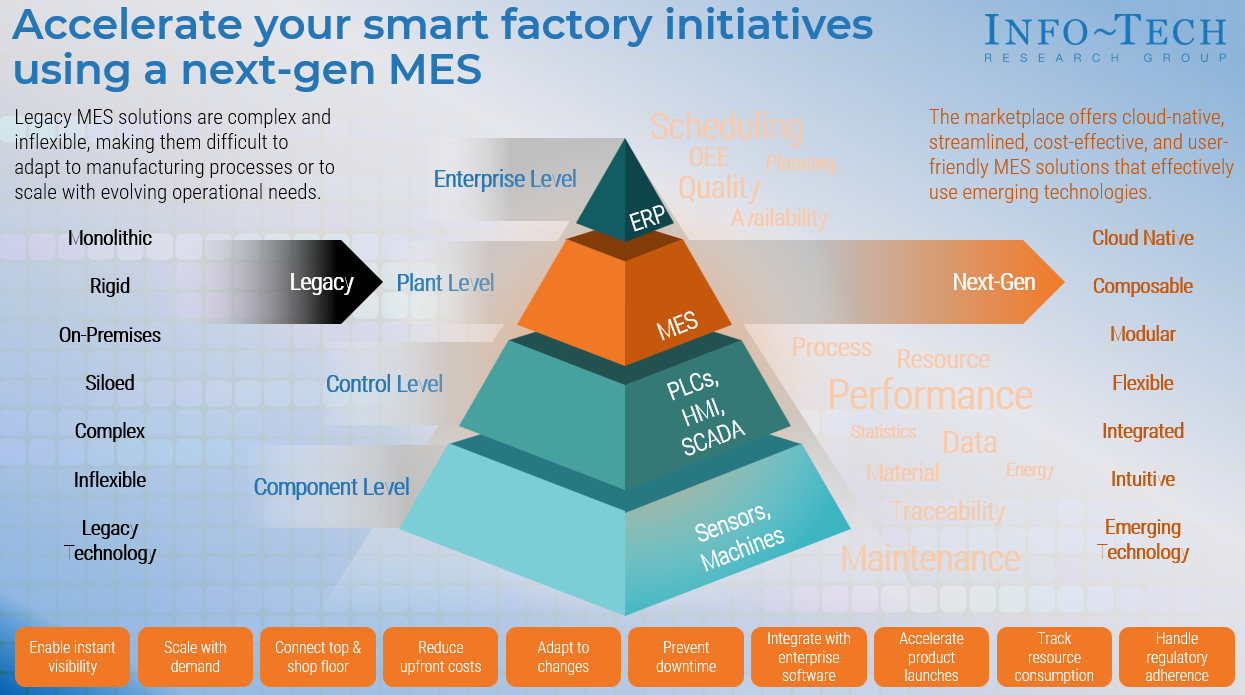
Legacy MES systems are complex, expensive, rigid, and time-consuming to customize. Until recently, manufacturers have had few alternatives to legacy MES systems. However, the landscape is now changing. The marketplace now offers more streamlined, cost-effective, and user-friendly MES solutions that can integrate seamlessly with existing systems and support real-time data access.
|
Manufacturers face several key issues with their legacy MES implementations: |
|
|---|---|
|
Complexity & rigidity |
Traditional MES solutions are complex and inflexible, making them difficult to adapt to manufacturing processes or to scale with evolving operational needs. |
|
High costs |
Deployment involves substantial initial investments and ongoing maintenance expenses, which can be financially burdensome. |
|
Poor integration |
Legacy MES systems do not seamlessly integrate with modern technologies or other enterprise systems, resulting in data silos. |
|
Unsatisfactory UX |
Traditional MES platforms feature complex user interfaces that are not intuitive, leading to user frustration and necessitating extensive training. |
|
Inadequate data freshness |
Legacy MES systems do not provide real-time data analytics, impeding manufacturers' ability to make timely decisions and respond swiftly to production issues. |
Source: Forbes, 2022
MES implementations have not been an easy exercise for manufacturers.
15-16 months is the average implementation time for a legacy MES1
1:5 is the ratio of license to service dollars spent on implementing a legacy MES1
~90% of small and midsize factories lack an MES2
1 - Tulip, 2021
2 - Pico CEO and Cofounder Ryan Kuhlenbeck, VentureBeat, 2022
Next-gen solutions need to address challenges and limitations of legacy MES solutions
Next-gen MES platforms must be modular, cloud-based, and fully integrated with enterprise systems, IIoT, and advanced technologies like AI. A next-gen MES must provide real-time data access, predictive analytics, and seamless automation while supporting zero-downtime maintenance. With an intuitive user interface and scalability, next-gen MES platforms must adapt to both high-volume and specialized manufacturing needs, driving cross-industry operational efficiency and flexibility.
|
Next-gen MES systems support diverse manufacturing needs and are relevant to a wide range of industries. Common capabilities include: |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1. Modular & Scalable |
2. Seamless Integration & Data Access |
3. Enhanced UX |
4. Zero Downtime |
5. Adaptability for Advanced Manufacturing |
|
|
|
|
|
Source: “MES of the Future Manifesto,” BioPhorum, 2022
Next-gen MES platforms are intended for manufacturers of all sizes.
“Legacy systems were designed for the complexities of the large manufacturers, making them expensive, difficult to use and requiring specialized support personnel.”
Source: Ryan Kuhlenbeck, Pico CEO and Cofounder, VentureBeat, 2022
Manufacturers are showing interest in next-gen MES platforms
As manufacturers pursue Industry 4.0 maturity, next-gen MES solutions are becoming a key driver for digital transformation and competitive advantage. Manufacturers are increasingly showing interest in next-gen MES platforms due to their ability to address the limitations of legacy systems, such as poor scalability, high costs, and integration challenges.
Next-gen MES platforms have the potential to revolutionize manufacturing processes.
Manufacturers using a next-gen MES have reported improvements across the board:
> 400% ROI over a three-year period
< 1 year to payback
> 10% improvement in productivity
> 20% fewer defects
> 30% faster defect correction rate
> 5% increase in quality
> $2 million savings in material costs
> $3 million top line revenue gain
> 10% improvement in delivery time
Source: Contributor interviews, 2024
Manufacturers plan to invest in MES platforms
46% of manufacturers are planning to increase their investment in MES over the next three years.
75% of manufacturers will have adopted MES by 2025.
63% of manufacturers believe that MES is essential for achieving Industry 4.0 capabilities.
Source: Worldmetrics, 2024
Projected MES investments by industry sector:
|
Automotive |
$5.2 billion by 2027 |
|
Aerospace & Defence |
$3.8 billion by 2027 |
|
Pharma & Life Sciences |
$2.5 billion by 2025 |
|
Energy & Utilities |
$1.8 billion by 2023 |
|
Packaging |
$2.5 billion by 2025 |
Source: Worldmetrics, 2024
MES platforms have evolved to incorporate support for emerging technologies
The evolution of MES has progressed from costly, monolithic mainframe systems to fully agile, cloud-native systems with seamless integration, autonomous decision-making, and zero downtime capabilities. Today, a variety of cloud-enabled MES platforms exist that effectively leverage IIoT, big data, and real-time analytics, offering manufacturers flexibility, scalability, and integration with enterprise systems.
|
Early 90s Monolithic |
2000 and later Server-based |
2010 and later Cloud-enabled |
Late 2010s Cloud-native |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
Outdated |
Traditional |
Current-gen |
Next-gen |
Source: Applied Control Engineering, 2023
CIOs should use key criteria to evaluate MES platforms holistically
Evaluate MES platforms based on predefined criteria to ensure there is clear understanding of its total cost of ownership, ease of implementation, and its ability to grow the business, improve operational efficiency, maintain system performance, and ensure business continuity.
|
Deployment How the MES is installed and maintained (on-premises vs. cloud) Important for understanding infrastructure needs, IT resources, and long-term management complexity. |
Cost Structure The upfront and ongoing costs associated with the MES Vital for budgeting and understanding the long-term financial commitment of the system. |
Technology Integration Compatibility with modern technologies (e.g. IIoT, AI/ML) Critical for future-proofing the MES and maximizing operational efficiency with advanced technologies. |
Accessibility Whether the system can be accessed remotely or only onsite Key for enabling flexibility in managing operations from different locations or on-the-go. |
|
Scalability The ease of expanding system capacity as the business grows Crucial for ensuring the MES can scale with business demands without excessive costs or delays. |
Updates How frequently the system is updated and how disruptive the process is Ensures the system stays current with minimal downtime, which impacts production continuity. |
Security How the system is protected from cyber threats Essential for safeguarding sensitive production and operational data, ensuring compliance and resilience. |
Time to Value The time it takes to implement the system and start seeing benefits A critical factor in understanding how quickly the MES can deliver ROI and operational improvements. |
|
Flexibility Ability to tailor the system to specific operational needs Key to ensuring the MES can adapt to unique processes and deliver the expected operational benefits. |
Data Access The ability to access real-time data and collaborate remotely Important for operational visibility, especially for decision-makers overseeing multiple locations. |
Disaster Recovery The system’s ability to recover from failures and data loss Important for maintaining business continuity and minimizing downtime during unexpected events. |
Implementation Method Implement a one-size-fits-all solution or prioritized capabilities first Important for developing capabilities based on business value in a flexible manner. |
Info-Tech Insight
Choosing the right implementation methodology (i.e. monolithic or composable) may be the most crucial step toward setting up an MES. The choice between the two methods should be given careful consideration.
While traditional MES platforms have been beneficial, they also have some limitations
MES platforms have always been beneficial to manufacturing organizations. However, traditional MES implementations have some critical drawbacks related to scalability, flexibility, complexity, and cost of modifying or maintaining the platform.
|
Criteria |
Traditional MES |
Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
|
Deployment |
On-premises deployment using local servers, requiring significant IT resources for setup and maintenance |
High complexity & overhead |
|
Scalability |
Requires hardware investments and long implementation times to scale |
Limited scalability |
|
Flexibility |
Customizations are expensive and time-consuming |
Low flexibility |
|
Cost Structure |
High upfront capital investments in hardware and software with recurring maintenance and customization costs |
High upfront costs |
| Maintenance |
Infrequent, slow, manual updates that require downtime and significant IT resources |
Costly updates |
|
Data Access |
Data is stored locally, making it harder to access remotely or collaborate across locations |
Limited real-time visibility |
|
Integration |
Difficult to integrate with modern technologies like IIoT, AI/machine learning (ML), and edge computing |
Limited adaptability |
|
Security |
Managed locally, requiring onsite security measures |
Limited security |
|
Disaster Recovery |
Disaster recovery and backups must be managed in-house, with slower recovery times in case of system failures |
Slow recovery |
|
Accessibility |
Limited to on-premises access; difficult to manage remotely or collaborate with global teams |
Limited accessibility |
|
Time to Value |
Implementation cycles often take months or years due to hardware setup and complex customization |
Long TTV cycles |
Traditional MES systems have a long lead time to value.
“…it could take up to four (4) years to integrate the traditional MES software with the hardware of the shop floor as it may require various modifications during the installation.”
Source: LiveTracking, 2021
Next-gen MES platforms improve on traditional MES platforms in several ways
Next-gen MES platforms improve on every performance criterion when compared to traditional MES platforms. While fully custom traditional MES platforms might still have a better fit with organizational requirements, next-gen MES platforms still outperform them on cost and time to value.
Criteria | Next-gen MES | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
Deployment | Hosted on the cloud, with no need for local infrastructure | Low complexity & overhead |
Scalability | Able to adjust resources quickly and scale operations easily | High scalability |
Flexibility | Easily customizable with modular features and APIs for rapid adaptation | High flexibility & modularity |
Cost Structure | Subscription-based pricing model with lower upfront costs | Predictable operating costs |
Maintenance | Automatic updates with little to no downtime, ensuring continuous delivery of new features and patches | Costly updates |
Data Access | Centralized data with real-time visibility from anywhere, enabling global collaboration and remote access | Near real-time visibility |
Integration | Easily integrates with IIoT, AI/ML, and other emerging technologies, making it ideal for Industry 4.0 environments | High integrability |
Security | Managed by the cloud provider with advanced, up-to-date security protocols and compliance standards | Advanced security |
Disaster Recovery | Managed by the cloud provider, offering more robust disaster recovery capabilities | Fast recovery |
Accessibility | Accessible from anywhere, allowing real-time monitoring and management from any device | Remote accessibility |
Time to Value | Time-to-value often achieved within months due to cloud infrastructure | Short TTV cycles |
Next-gen MES systems work well with advanced technologies.
“End users are increasingly adopting cloud MES as it allows them to take advantage of the latest IoT technologies and offers better scalability than on-premises MES systems.”
Source: IOT Analytics, 2021
Next-gen MES platforms are critical for driving specific manufacturing objectives & benefits (1/2)
|
Leading use cases for next-gen MES platforms (Order does not reflect importance) |
Value Drivers |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Ops. Efficiency |
Business Growth |
Customer Experience |
Employee Experience |
Risk & Resilience |
ESG |
||
|
Real-Time Production Monitoring |
Enables real-time production monitoring using IIoT sensors, resulting in optimized workflows and faster issue resolution |
✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
|
Predictive Maintenance |
Enables predictive maintenance using AI/ML, resulting in reduced downtime and extended equipment life |
✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
|
OEE Improvement |
Improves overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) using real-time analytics, resulting in enhanced productivity |
✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
|
Cycle Time Reduction |
Enables cycle time reduction using workflow automation, resulting in increased throughput and output |
✓ | ✓ | ||||
|
Energy Consumption Optimization |
Enables energy usage optimization using energy monitoring tools, resulting in cost savings and sustainability gains |
✓ | ✓ | ||||
|
Production Planning Optimization |
Enables optimized production planning using real-time data and AI, resulting in better resource allocation |
✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
|
Automated Quality Control |
Enables automated quality control using machine vision and AI, resulting in higher quality and fewer defects |
✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
|
Compliance Automation |
Enables compliance tracking and automation using integrated regulatory databases, resulting in reduced compliance risk |
✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
|
Supply Chain Visibility |
Enables supply chain visibility using integrated data analytics, resulting in more accurate demand fulfillment |
✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
|
Inventory Management |
Optimizes inventory management using real-time tracking, resulting in reduced stock levels and improved turnover |
✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
|
Remote Production Monitoring |
Enables remote production monitoring using cloud connectivity, resulting in enhanced uptime and flexibility |
✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
Next-gen MES platforms are critical for driving specific manufacturing objectives & benefits (2/2)
Leading use cases for next-gen MES platforms (Order does not reflect importance) | Value Drivers | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Ops. Efficiency | Business Growth | Customer Experience | Employee Experience | Risk & Resilience | ESG | ||
Downtime Reduction | Reduces downtime using predictive analytics, resulting in improved production efficiency and lower costs | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
Capacity Planning | Enables capacity planning using historical and real-time data, resulting in optimized production scalability | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
Custom Order Processing | Enables custom order processing using workflow customization tools, resulting in enhanced customer satisfaction | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
Product Traceability | Enables product traceability using blockchain technology, resulting in secure, compliant, and transparent production | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
Remote Work Enablement | Enables remote work enablement using mobile access, resulting in greater flexibility for employees | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
Sustainability Reporting | Enables sustainability reporting using environmental data tracking, resulting in improved compliance and ESG reporting | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
Real-Time Collaboration | Enables real-time collaboration using shared data dashboards, resulting in improved cross-functional alignment | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
Customer Order Transparency | Enables customer order transparency using real-time status updates, resulting in improved customer trust | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
Automated Data Analytics | Enables automated data analytics using AI, resulting in continuous process improvement and decision-making support | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
Training & Skill Management | Enables training and skill tracking using integrated HR tools, resulting in safer operations and better compliance | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
Predictive Supply Chain | Enables predictive supply chain management using AI insights, resulting in proactive disruption handling | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
Glossary of important acronyms
This slide serves as a comprehensive glossary of MES-related acronyms used in this research.
- AIM – Advanced inventory management
- BI – Business intelligence
- CAD – Computer aided design
- CAE – Computer aided engineering
- CAM – Computer aided manufacturing
- CMMS – Computerized maintenance management system
- COM – Common object model
- CRM – Customer relationship management
- DHR – Device history records
- EAM – Enterprise asset management
- ERP – Enterprise resource planning system
- HRMS – HR management system
- LIMS – Laboratory information management system
- MQTT – Message queuing telemetry transport
- OEE – Overall equipment efficiency
- OPC/UA – Open platform communications/ unified architecture
- PLC – Programmable logic controller
- PLM – Product lifecycle management
- QMS – Quality management system
- REST – Representational state transfer
- S&OP – Sales & operations planning
- S&OE – Sales & operations execution
- SCADA – Supervisory control & data acquisition
- SKS – Stock keeping system
- SKU – Stock keeping unit
- SQDC – Safety, quality, delivery & cost
- TMS – Transport management system
- WMS – Warehouse management system
Organizational Functional Model for Next-Gen MES
This organizational functional model of an MES is an illustrative representation of the platform’s core functions, advanced capabilities, and integration with shop floor and corporate systems. On a next-gen MES platform, all core services are hosted on a cloud platform.

Integration with other critical enterprise applications is key
A next-gen MES must integrate with several other systems in the manufacturing value chain. This enables automated sharing of critical information between top floor and shop floor, enabling alignment with organizational and operational objectives.

This list is illustrative and not meant to be exhaustive.
Acronyms explained on Slide 14.
|
System |
Data shared to MES |
Data shared from MES |
|---|---|---|
|
ERP |
Production schedules, inventory levels, order requirements, cost data |
Production progress, inventory updates, job completion statuses, labor tracking |
|
S&OP/ S&OE |
Demand forecasts, supplier lead times, logistics schedules |
Real-time production status, material usage, inventory needs for reorder |
|
PLM |
Product designs, bills of materials (BOMs), engineering changes |
Production feedback, quality data, design compliance reports, process deviations |
|
CAD/E/M |
2D/3D models, assembly instructions, specifications, simulation results, material properties, machining parameters |
Design issues, quality data, tolerances, material behavior, deviations, cycle times, scrap data |
|
QMS |
Quality standards, test requirements, compliance data |
Quality control results, defect rates, noncompliance incidents, corrective actions |
|
CMMS |
Equipment maintenance schedules, historical maintenance data |
Real-time equipment status, production impact of maintenance activities, predictive maintenance alerts |
|
CRM |
Customer orders, delivery expectations, custom order specifications |
Order status updates, production progress, estimated completion times, quality assurance confirmations |
|
WMS |
Inventory location, picking and packing instructions, shipping status |
Finished goods inventory, production yields, component needs for restocking |
|
HRMS |
Employee roles, certifications, training records, shift schedules |
Labor hours, machine operation logs, skill utilization, training needs |
|
SCADA |
Real-time machine performance, process control parameters |
Process instructions, alerts for operator actions, production targets |
|
EAM |
Equipment life cycle data, asset status, maintenance schedules |
Real-time asset usage, equipment efficiency data, maintenance triggers |
|
EMS |
Energy consumption targets, emissions standards |
Energy consumption per unit, process energy efficiency, alerts on abnormal energy use |
|
BI Tools |
Production and operational data for reporting, historical analysis |
Process KPIs, performance trends, efficiency metrics, resource utilization |
|
TMS |
Shipping schedules, transportation modes, delivery commitments |
Order completion updates, shipment preparation status, real-time production updates affecting delivery |
Integration is crucial for an MES to coordinate information across functions
Effective MES integration enhances productivity, improves quality, and ensures seamless coordination across the enterprise. Given the scope of MES capabilities, integration with other corporate IT systems has an impact on planning, supply chain functions, product, quality, maintenance, inventory, resource utilization, customer relationship, and the energy footprint of the organization.
System | Reasons to Integrate | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
ERP | Aligns manufacturing operations with production planning, inventory, and financial tracking | Synchronizes production schedules, real-time inventory tracking, better cost control |
S&OP/ S&OE | Manages supply chain activities (demand forecasting, logistics, supplier management) | Optimized supply chain flows, reduced lead times, improved supplier collaboration |
PLM | Handles design, development, and engineering, ensuring smooth transitions from design to manufacturing | Real-time updates, better quality control, faster time to market |
CAD/E/M | Creates design-to-production workflow, designs and machining optimization | Minimum errors, faster prototyping, optimized production cycles, process adjustment |
QMS | Automates quality checks and ensures compliance with industry standards | Automated quality assurance, reduced defects, compliance with standards (ISO, FDA, etc.) |
CMMS | Monitors machine health and schedules maintenance based on real-time data | Minimizes downtime, extends equipment life, improves production planning |
CRM | Aligns production schedules with customer demand and order fulfillment | Real-time order status, improved customer satisfaction, demand-driven production planning |
WMS | Manages storage, picking, packing, and shipping of goods | Faster inventory management, efficient order fulfillment, reduced waste and idle time |
HRMS | Manages employee data, work schedules, and certifications for operational safety | Ensures compliance, manages certifications, optimizes workforce scheduling |
SCADA | Provides real-time monitoring and control of shop floor operations | Real-time process control, integration of machine-level data, faster response to issues |
EAM | Tracks and manages production assets and maintenance tasks | Maximizes asset utilization, prevents downtime, reduces total cost of ownership |
EMS | Tracks and optimizes energy consumption linked to production processes | Optimizes energy use, achieves sustainability goals, identifies energy-intensive processes |
BI Tools | Analyzes data to provide insights into production performance and efficiency | Data-driven decision-making, process improvement, enhanced reporting and analysis |
TMS | Manages logistics, shipping, and transportation | Streamlines logistics, lead times, enables synchronization between production and shipping |
This list is illustrative and not meant to be exhaustive.
Acronyms explained on Slide 14.
Next-gen MES platforms use emerging technologies in impactful ways
Next-gen, cloud-native MES platforms are integrating with key emerging technologies such as IIoT, Big Data, AI, and 5G. These integrations enable advanced functionalities like real-time data monitoring, predictive analytics, and decentralized production, driving operational efficiency, precision, and scalability.
|
IIoT Next-gen MES gathers real-time data from machines via IIoT sensors, and devices. Enables real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and process optimization |
Big Data Next-gen MES platforms procure, process, and analyze large production data sets. Provides insights for process optimization, trend analysis, and demand forecasting |
AI/ML Next-gen MES use embedded AI/ML algorithms for predictive analytics. Enables predictive maintenance, quality improvements, and process optimization |
|
VR/AR Next-gen MES supports integration with VR/AR for operator training and maintenance assistance. Enhances visualization of complex processes, guides maintenance tasks, and reduces errors |
Edge to Cloud Next-gen MES leverages edge computing for local data processing while connecting machines to the cloud. Improves real-time decision-making on the shop floor with cloud-based analytics scalability |
Blockchain Some next-gen MES systems can integrate with blockchains for secure, immutable production tracking. Ensures transparency, compliance, and product authenticity in regulated industries |
|
Additive Manufacturing Next-gen MES platforms can incorporate 3D printing workflows with traditional production. Enables customized, small-batch production, and rapid prototyping, and reduces lead times and waste. |
Robotics Next-gen MES platforms can coordinate with robots and automation systems to streamline workflows. Improves precision, consistency, and efficiency by managing both robotic and human operators |
Wireless Connectivity Next-gen MES integrates with 5G/Wi-Fi 6 hardware for high-speed, low-latency factory floor connectivity. Enhances real-time data exchange, enabling flexible, decentralized production setups and operational agility |
New technologies significantly enhance the effectiveness of MES platforms.
“… a combination of a Manufacturing Execution System (MES) and AI has accelerated production processes in manufacturing by up to 10% and reduced planning time by up to 50%.”
Source: Vernaio Blog, 2024
Email Infographic
About Info-Tech
Info-Tech Research Group is the world’s fastest-growing information technology research and advisory company, proudly serving over 30,000 IT professionals.
We produce unbiased and highly relevant research to help CIOs and IT leaders make strategic, timely, and well-informed decisions. We partner closely with IT teams to provide everything they need, from actionable tools to analyst guidance, ensuring they deliver measurable results for their organizations.
What Is a Blueprint?
A blueprint is designed to be a roadmap, containing a methodology and the tools and templates you need to solve your IT problems.
Each blueprint can be accompanied by a Guided Implementation that provides you access to our world-class analysts to help you get through the project.
Talk to an Analyst
Our analyst calls are focused on helping our members use the research we produce, and our experts will guide you to successful project completion.
Book an Analyst Call on This Topic
You can start as early as tomorrow morning. Our analysts will explain the process during your first call.
Get Advice From a Subject Matter Expert
Each call will focus on explaining the material and helping you to plan your project, interpret and analyze the results of each project step, and set the direction for your next project step.
Unlock Sample ResearchAuthor
Shreyas Shukla
Contributors
- Kristin McLane, CEO, CIMx
- Jarda Smrz, Independent Expert, PINpoint MES
- Marc Seguin, Independent Expert, PINpoint MES
- Warren Andrade, Independent Expert, PINpoint MES
- Melanie Davy, VP, Sales, PINpoint MES
- Jennifer Epstein, Director, Sales Enablement, PINpoint MES
- Scott Ryan, Consultant, Cetec ERP
- Ryan McMartin, Independent Expert, Parsec
- Jason Halpern, Independent Expert, Manufacturing Solutions Company
- Anonymous, Independent Expert, Manufacturing Software Implementer
- Anonymous, Manager, Supply Chain & Network Operations, Specialist Consulting Firm
Unlock Accelerate Your Smart Factory Initiatives Using a Next-Generation MES
Get Instant Access
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.
This content is exclusive to members.
Get instant access by signing up!
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.
Search Code: 106828
Last Revised: February 13, 2025
Book an Appointment
IT Research & Advisory Services
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.








