Bring Your Factory to Life With Smart Manufacturing 5.0
Using human-technology synergy to drive exponential growth and productivity.
- Products need to be produced on time.
- Collaborative processes are vital.
- Machines and humans need to work together safely and effectively.
- Evolution is speeding up and the competitive market is elevating the priority of digital transformation activities to produce a Smart Manufacturing 5.0 environment.
Our Advice
Critical Insight
- The next evolution, Industry 5.0, also known as Smart Manufacturing 5.0, is currently underway, and it is more important than ever to integrate technology and people. To attain exponential growth or maintain market share against competitors who have already done so, businesses must start focusing on Smart Manufacturing 5.0 and adopt Industry 4.0 tools and technologies.
- They must enable technology with a human satisfaction and environmental sustainability perspective.
Impact and Result
- Predict any potential problems or roadblocks.
- Enable higher levels of collaboration and quality.
- See greater efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Bring Your Factory to Life With Smart Manufacturing 5.0 Research & Tools
1. Bring your Factory to Life with Smart Manufacturing 5.0 Storyboard – Leverage Industry 5.0 to power a human-technology constructive collaboration.
Using innovative tech, a focus on people, resilience, intelligence, and sustainability, Smart Manufacturing 5.0 will enable you to provide top-notch customized products, exponentially boost productivity and growth, and achieve long-term growth and a competitive edge in the market.
Bring Your Factory to Life With Smart Manufacturing 5.0
Using human-technology synergy to drive exponential growth and productivity.
Analyst Perspective
Blending human and machine to go beyond the foundations of Industry 4.0.
Throughout the evolution of industry from 1.0 to 4.0, we have seen major industrial changes that have significant impacts on the strategic decisions being made by business.
Since Industry 4.0 was first introduced at Hannover Fair 2011 by German Chancellor Angela Merkel, the activity levels surrounding Industry 4.0 are now in full swing. Most businesses have now achieved some level of implementation that includes Industry 4.0 technology usage with Cloud services being the one most widely adopted within businesses.
Now that we are in the midst of the next evolution (Industry 5.0, Smart Manufacturing 5.0), integrating technology and people has become crucial. Businesses must embrace Industry 4.0 tools and technologies and begin to focus on Smart Manufacturing 5.0 if they hope to achieve exponential growth or protect their market share from competitors who are doing so.
A more rapid adoption of Smart Manufacturing 5.0 and Industry 5.0 than of Industry 4.0 is anticipated, in my opinion, due to the widespread acceptance of the integration of AI, ML, and humans as an essential component of any successful business model that prioritizes sustainability, quality, efficiency, and the wellbeing of employees.

Kevin Tucker
Principal Research & Advisory Director, Industry
Manufacturing, Supply Chain, Logistics, and Transportation
Info-Tech Research Group
Executive Summary
Your Challenge
- Gaining support for Smart Manufacturing 5.0 when most haven't achieved Industry 4.0. Many companies aren't yet sold on the merits of advanced technologies because they primarily only focus on product fabrication technologies.
- Ensuring that advanced technologies are implemented in a responsible way that considers how they must be integrated and that the data must be free from bias and hallucinations because AI is at the center of this new wave.
- It's difficult for many businesses to envision Manufacturing 5.0 due to legacy systems that still hoard a lot of their time.
Common Obstacles
- Integrating new technologies with existing systems and machinery while ensuring compatibility with various components, sensors, machines, and other software solutions that are off-the-shelf or homegrown.
- Uplifting workforce skills and change management to overcome the skill gaps and employee resistance.
- Handling massive volumes of data from IoT sensors while ensuring accuracy, security, and compliance.
- Budgeting for costs and return on investment (ROI) as companies will struggle with justifying the upfront investment in Smart Manufacturing 5.0 technology.
Info-Tech's Approach
- We recommend identifying some specific use cases that are most applicable to the needs of your organization and will offer the best short-term benefits.
- Use this report to help determine where the value proposition can help elevate your business case for change.
- Create collaborative partnerships with industry peers, technology companies, and experts who can provide guidance.
- We work closely with our customers to provide both strategic and tactical decision-making advisory services.
Info-Tech Insight
Many forward-thinking companies have already been thinking about and experimenting with Smart Manufacturing 5.0 technologies as advanced manufacturing capabilities have started to become key differentiators in the market and necessary for meeting customer's demands for more transparent processes.
Manufacturing through the centuries
The evolutionary progression from Industry 1.0 to Industry 5.0 encompasses various stages of development.
Smart Manufacturing 5.0
Industry 4.0 Technologies + Industry 5.0 Concepts = Smart Manufacturing 5.0
|
Dull, Dangerous, and Dirty |
Electrical Assembly Lines |
Computerized Automation |
Robotic Cybersystems |
Human-Machine Synergy |
|---|---|---|---|---|

|
||||
|
Mechanized Manufacturing Steam Engine Power Centralized Factories The First Working Class |
Electrical Power Telegraph & Telephone Internal Combustion Engine Mass Production Systems |
Computer Control Systems Automation Electric Controlled Sensors *PLC Machine Controls |
Advanced Technology IoT, 3D Print, AR/VR, Robotics, Digital Twin, AI, ML, NLP, Big Data Analytics, Cloud Cybersecurity |
Human-Machine (Cobotic) Plant Process Digitization Dynamic Personalization Sustainability |
*Programmable logic controllers (PLC) use programming to control machines based on sensor data.
Industry 5.0 is a shift away from a purely technology focus
The goal of Industry 5.0 is to evolve away from being purely technology-centric and gain more ground on the human factors and environment through:
- Human-Centricity: Transforms people from resources to assets. Instead of people serving organizations, organizations will serve people. Instead of using talent to create a competitive advantage and value for customers, Industry 5.0 adds value to attract and retain the best workers.
- Resiliency: As the world becomes more interconnected, COVID-19 and supply shortages spread. Many companies prioritize profits and efficiency, but they hurt resilience. Agile and flexible businesses may be less resilient, say some. Instead of focusing on growth, profitability, and efficiency, resilient firms prepare for and respond to crises.
- Sustainability: Takes sustainability beyond reducing, minimizing, or mitigating climate damage to actively promoting change. This goal, also known as "net positive" or "carbon neutrality," seeks to improve the world by making companies part of the solution rather than just "greenwashing."
"Yes, excessive automation at Tesla was a mistake. To be precise, my mistake. Humans are underrated."
– Elon Musk, Founder, CEO, and Product Architect, Tesla, Inc.
The terminology and usage differences are subtle
Industry 5.0: A significant shift away from just being a technically-driven evolution. This generation elevates the importance of collaboration between humans and advanced technologies. AI combined with robotics to consider the overall wellbeing for society vs. being efficiency-, production-, and profit-focused. The three key pillars are human-centricity, sustainability, and resilience.
Smart Manufacturing 5.0: Things get a little confusing because Industry 5.0 and Manufacturing 5.0 are terms that are frequently used interchangeably. However, this report focuses on the manufacturing sector and discusses how Industry 5.0 principles would combine cutting-edge technologies with a human-centric approach that incorporates sustainability and resilience. However, it goes beyond this to include intelligence in order to deliver the best customized products, leading to long-term growth and a competitive edge in the market.
Factory 5.0: This is a less commonly used term that depicts the use of Industry 5.0 principles in the factory for the integration that is less about digital transformation and more about ensuring the human element is being considered at every stage.
Smart Manufacturing 5.0 leverages Industry 5.0

|
ATTRIBUTES OF INDUSTRY 5.0 |
|
Info-Tech Insight
The goal of Smart Manufacturing 5.0 is to combine the best of Industry 4.0 with the attributes of Industry 5.0 to create solutions that are cyberphysical, mass-customizable, collaborative, cognitive, and environmentally friendly.
Smart Manufacturing 5.0 is a cobotic environment
The term "collaborative robot" was initiated by James E. Colgate and Michael A. Peshkin in 1996 and refined by The Wall Street Journal as "cobot."
Almost 30 years after the idea of collaborative robots was initiated, we are only now starting to really leverage the true potential of human-machine interaction.
We now understand that cobotic offers a wide range of interactions between humans and machines. In many cases, the machines are vastly more intelligent and offer us a combination of productivity, quality, and safety for the human counterpart.
Synchronized operations enable shared workspaces that may be interactive or entail both human and robot carrying out distinct tasks within a confined space.
We are no longer just imaging the blending of humans and robots. Now we have what seems like an unlimited number of opportunities and the struggle is to get our eyes opened wide enough to see the potential of cobotic operations.
Smart Manufacturing 5.0 is critical for success
Investment has accelerated; however, the results are coming slowly.
|
CEOs currently investing in digital technologies: |
Worldwide employee reskilling by 2025: |
Surveyed manufacturers who believe smart factories will be the main driver of competition by 2025: |
Dismal percent reporting at least one fully converted smart factory: |
|---|---|---|---|
80% |
50% |
86% |
5% |
|
Source: Birlasoft, 2023 |
Source: World Economic Forum, 2020 |
Source: Deloitte, 2020 |
Source: "Optimize operating models," Deloitte, 2023 |
Few have fully converted to smart manufacturing
Conversion has challenges; the industry cannot change at the same speed due to differing states:
- Legacy IT and business systems create complications for the integrations because the data and application interfaces are not designed around modern principles.
- Budget, costs, and resource scarcity are problematic because technical debt often needs to increase in the short term and there is an extensive retraining requirement.
- Worker and market skills gap is a major issue. The market hasn't caught up, and certain skills, like data science, are costly and difficult to find.
- Change management and cybersecurity are vital for success and most companies aren't ready for either of these as machines and people need to change in tandem.
Smart manufacturing has caught the attention of manufacturers, but adoption has been modest. Without a transition plan and the right technologies in place, small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) may struggle to adopt the smart factory model.
| Percentage of manufacturers who have embraced smart manufacturing. | 5% |
Source: "Optimize operating models," Deloitte, 2023
Smart Manufacturing 5.0 is a value creator for all types of manufacturing businesses
Although Smart Manufacturing 5.0 is still in its infancy, it has already demonstrated that it will drive exponential change across industries.
|
Machine-Human Collaboration |
It makes it possible for people and machines to work together, bringing out the best in each to make unique, tailored goods and services. |
|---|---|
|
Helps the Environment |
By maximizing resource utilization, decreasing waste, and enhancing energy efficiency, it lessens the environmental effect of manufacturing. |
|
Improved Safety and Quality |
It reduces hazardous or repetitive tasks, provides real-time feedback and guidance, and encourages creativity and learning to improve worker safety and quality. |
|
Dynamic Adaptability and Resiliency |
As a result, the manufacturing system is better able to withstand and adjust to external shocks, fluctuating market conditions, and evolving consumer demands. |
|
Real-Time Insights |
It creates insights and answers for difficult manufacturing problems by combining the power of artificial intelligence, big data, and cloud computing. |
"[Dr.] Malshe envisions Industry 5.0, which will be human- and earth-centric and will be true smart manufacturing by and for humans in harmony with the planet."
– SME, 2020; Dr. Ajay P. Malshe is a Distinguished Professor of Mechanical Engineering, Purdue University
Smart Manufacturing 5.0 has significant employee experience potential
01 – An Enhanced Work-Life Balance: Having greater degrees of remote work, flexible work arrangements, telecommuting, and remote monitoring tools will help employees manage their personal and professional commitments and thereby reduce stress and enhance wellbeing.
02 – Advanced Tools, Training, and Skills Development: Advanced technologies create the need for upskilling and continuous learning of cutting-edge tools that will in turn offer the employee a greater sense of accomplishment and self worth.
03 – An Empowering and Collaborative Work Environment: The synergy created through cobotic and AI systems fosters a collaborative approach to having human-machine interactions for solving complex business problems together.
04 – Data- and Incentive-Driven Performance and Recognition: The vast amounts of data used to enable data-driven decision-making is also utilized to offer a more objective view into employee/machine performance which foster a culture of fairness and transparency.
Smart Manufacturing 5.0 offers customer-centric experiences
01 – Improved Product Quality and On-Time Delivery: Having greater degrees of remote work, flexible work arrangements, telecommuting, and remote monitoring tools will help employees manage their personal and professional commitments and thereby reduce stress and enhance wellbeing.
02 – Rapid Ability to Respond to Customer Demands: Manufacturing 5.0's dynamically flexible production systems enable the business to provide almost immediate adaptiveness and thereby offer shorter lead times and faster delivery without compromising on product quality.
03 – Personalization and Customization of Product/Processes: Products and processes can be dynamically tailored toward the customers' preferences to offer them a more customized and satisfying experience. Every customer gets a uniquely positive experience that is continuously enhanced through the smart manufacturing process.
04 – Enhanced Product Traceability and Transparency: Customers want to know where and when the product will be available for them. New solutions such as mobile and radio frequency identification methods help to ensure they can be tracked from raw material processing through to delivery and acceptance.
Smart Manufacturing 5.0 and the user experience factor
The goal of user-centered design (UCD) is to fully understand customer needs that will in turn maximize shared value.
- User challenges encountered in the factory are often highly complex for both the operator and those that are trying to provide solutions.
- A solid interaction between the user (operator) and the technical team is vital for navigating through the mix of legacy and Industry 4.0 technologies that are used to produce Industry 5.0 personalization.
- In this industry evolution to 5.0, the user experience takes center stage as we focus back on a human-centric approach of using advanced machine-based solutions that complement the work being done by humans (working in harmony with each other).
People may see this as a regressive move, but it's actually a refactoring to accommodate the inevitable escalation of human-machine interactions and the subsequent need for a serene synergy to ensure their safe and efficient collaboration.
Source: Etteplan, 2024.
"Expectations towards tools and services used at work are based on apps that everyone's using in their personal lives: People want user-friendliness, intuitiveness and personified user experiences – the chance to do everything efficiently and pleasantly. Demands continue to grow all the time."
– Hanna Remula, Head of Design, Cloud and Applications, Etteplan
AI is everywhere but not always visible
AI is becoming a key contributor to the smart manufacturing solution market, so you need to understand how to deliver impact.
|
AI Impact |
|
|---|---|
|
1 Be Intentional |
Being very clear about the important factors (policy, transparency, ethics, accountability, safety, accuracy requirements, etc.) for all AI solutions adoption. |
|
2 Identify Embedded AI |
The product AI embedded into, and you may not be able to directly interact, configure, or influence it. |
| 3 Unmask Invisible AI |
The product has AI embedded into it, but you can't see or touch any aspect of the AI capabilities. |
| 4 Fix Hallucinations |
Incorrect or misleading information generation and related deception, such as AI pretending to be human, must be tightly managed. |
| 5 Enforce Responsible AI |
Companies must learn how to build, buy, and deploy AI solutions that are trusted internally/externally and educate the business on its responsible use. |
The best use of AI is to have an "intentional" approach to AI usage across the organization.
Info-Tech's approach and team can help irrespective of where you are in your transformation journey
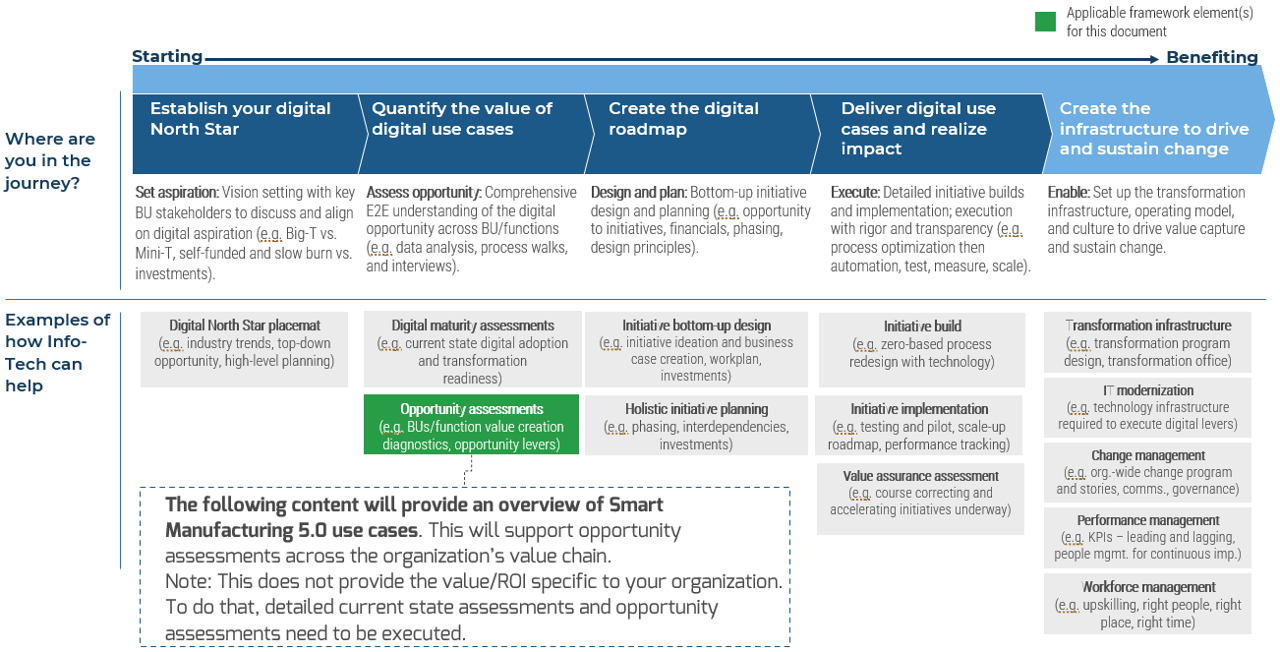
Measure the value of this document
Document objective
Demonstrating exemplary use cases can serve as a springboard for further brainstorming and planning as you construct a new business case to fund a variety of Smart Manufacturing 5.0 projects.
Measuring your success against that objective
You can gauge how well your initiative pipeline is developing using a variety of qualitative and quantitative, direct and indirect metrics. Several instances of this include:
- Enhanced pipeline value for initiatives.
- The number of capacities that the initiative pipeline affects.
- Improved comprehension of the impact of initiatives in relation to the organization's capability map.
- A deeper comprehension of the valuable sources that the organization's initiative pipeline is addressing or not addressing.
See Establish Your Digital Transformation Governance in the Digital Transformation Center for more details
Smart Manufacturing 5.0 Use Case Library Methodology
SECTION 1
What is a Smart Manufacturing 5.0 use case?
A Smart Manufacturing 5.0 use case is a combination of Industry 4.0/5.0 technologies and principles applied to a specific capability of the manufacturing operations of the business within a given industry/function to create value.
Use case
Industry or function
The relevant industry or function (many use cases will apply across multiple industries/functions).
Capabilities
The activities or job(s) to be done that your organization performs to ultimately deliver a product or service.
Industry 4.0/5.0 technology & business integration principles
The base technology that enables value-creating performance gains.
The Smart Manufacturing 5.0 use case report
What is it?
A Smart Manufacturing 5.0 use case represents a scenario where a business has leveraged advanced industry technology, human-centricity, sustainability, and resilience within their manufacturing capabilities to elevate their business beyond Industry 4.0 capabilities.
Why is it important?
In the context of a digital strategy, the Smart Manufacturing 5.0 use case library:
- Determines the environment, people, and technologies' strategic importance to the operation and their potential value sources to be examined in a top-down opportunity assessment.
- Dismantles the manufacturing operation's silo approach and emphasize the significance of Smart Manufacturing 5.0 as one of the fundamental building blocks of the initiatives that will eventually provide value to the company.
Email Infographic
About Info-Tech
Info-Tech Research Group is the world’s fastest-growing information technology research and advisory company, proudly serving over 30,000 IT professionals.
We produce unbiased and highly relevant research to help CIOs and IT leaders make strategic, timely, and well-informed decisions. We partner closely with IT teams to provide everything they need, from actionable tools to analyst guidance, ensuring they deliver measurable results for their organizations.
What Is a Blueprint?
A blueprint is designed to be a roadmap, containing a methodology and the tools and templates you need to solve your IT problems.
Each blueprint can be accompanied by a Guided Implementation that provides you access to our world-class analysts to help you get through the project.
Talk to an Analyst
Our analyst calls are focused on helping our members use the research we produce, and our experts will guide you to successful project completion.
Book an Analyst Call on This Topic
You can start as early as tomorrow morning. Our analysts will explain the process during your first call.
Get Advice From a Subject Matter Expert
Each call will focus on explaining the material and helping you to plan your project, interpret and analyze the results of each project step, and set the direction for your next project step.
Unlock Sample ResearchAuthor
Kevin Tucker
Contributors
- Peter De Villiers, Group Head: IT Strategy & Planning, Coca Cola Beverages Africa
- Stuart Howard, CTO, Goodyear Tire Company
Unlock Bring Your Factory to Life With Smart Manufacturing 5.0
Get Instant Access
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.
This content is exclusive to members.
Get instant access by signing up!
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.
Search Code: 104560
Last Revised: May 1, 2024
TAGS:
Smart Manufacturing 5.0, Industry 5.0 collaboration, Factory 5.0 human-centric, cyber-physical factory, industrial cybersecurity, AI in manufacturing, machine learning industrial applications, augmented reality in factories, Internet of Things industry, IoT industry, big data in smart manufacturing, human-robot collaboration, adaptive manufacturing systems, digital transformation in industry, smart factory innovation, human-machine interface, sustainable manufacturing 5.0, personalized production, advanced automation, collaborative robots, cobots, cobotic, Factory 5.0 adaptability, employee skill development in industry, Industry 5.0 societal value, cybersecurity in smart manufacturing, IoT and Industry 5.0, robotics in advanced manufacturing, efficiency in Factory 5.0, productivity in smart industry, future of manufacturing, smart systems in industry, quality assurance, quality testing, virtualization in manufacturingBook an Appointment
IT Research & Advisory Services
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.
Speak With A Representative
Request Content Access
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.








