Consider Agile for Banking
Understanding the core elements of Agile and its suitability with other methodologies in banking.
There is constant pressure on your bank to deliver new products and services to remain competitive with a growing number of market participants:
- Your customers increasingly expect you to understand their unique and constantly changing needs.
- The banking industry is increasingly reliant on technology, which has dramatically increased the need for effective communication between IT and the business.
Our Advice
Critical Insight
- Your bank’s processes are rigid and likely based on older Waterfall development methodologies that required extensive upfront design effort.
- Waterfall follows a sequential, inflexible development path that doesn't easily accommodate changes throughout the development process.
- Your bank has a complex and hierarchical structure with a culture that does not promote ongoing communication, collaboration, or openness to change.
Impact and Result
For many banks, the Waterfall development approach is still relevant due to the highly regulated nature of the industry and its products and services. Agile can be used in certain areas of your bank in conjunction with Waterfall if you:
Consider Agile for Banking Research & Tools
1. Consider Agile for Banking Deck – Understand the Agile methodology/SAFe 6.0 in the context of retail banking.
The retail banking industry is struggling with its core banking systems, especially their digital front ends that drive their customers' online and mobile banking experiences. COVID-19 caused a rapid acceleration in customer adoption of online and mobile banking and customers now expect much more advanced capabilities and experiences. Core banking vendors are behind and struggling to catch up. This work presents four common approaches to modernization based on 12 specific criteria.
2. Scaled Agile Readiness Assessment – Use this tool to conduct an Agile readiness survey.
Determine your bank's readiness to implement Agile using our five-part criteria.
Member Testimonials
After each Info-Tech experience, we ask our members to quantify the real-time savings, monetary impact, and project improvements our research helped them achieve. See our top member experiences for this blueprint and what our clients have to say.
9.0/10
Overall Impact
Client
Experience
Impact
$ Saved
Days Saved
Testimonial
Jamaica National Group Ltd.
Guided Implementation
9/10
N/A
N/A
Best: it brought to the forefront additional factors to consider and improve our agile delivery.
Consider Agile for Banking
Understanding the core elements of Agile and its suitability with other methodologies in banking.
Analyst Perspective
Banks are using Agile selectively to drive value
Agile has been around for over 20 years and has transformed software development and business models. It has become an important methodology to help businesses within rapidly changing markets respond quickly with competitive products and services.
Despite the overwhelming adoption of Agile across many industries, it has not been fully embraced in the retail banking industry. As Agile was adopted, industries that were highly regulated began to recognize that its principles did not always align with high levels of regulation. With its roots as a software development methodology, Agile has also struggled in environments where there are significant amounts of legacy technology and/or high complexity.
Finally, Agile is as much a philosophy as it is a collection of procedures and processes. Large, complex, and well-established businesses such as banks tend to have hierarchical management structures and rigid technology that don't align well with Agile's cultural requirements.
Despite these challenges, there are opportunities for banks to implement Agile and realize significant benefits. While broad-based adoption is likely impractical, many banks are combining traditional Waterfall methods with Agile to increase customer centricity.

David Tomljenovic MBA LLM CIM
Head of Financial Services Industry Research
Info-Tech Research Group
Executive Summary
| Your Challenge | Common Obstacles | Info-Tech's Approach |
|
There is constant pressure on your bank to deliver new products and services to remain competitive with a growing number of market participants. Your customers increasingly expect you to understand their unique, constantly changing needs. The banking industry is increasingly reliant on technology, which has dramatically increased the need for effective communication between IT and the business. |
Your bank's processes are rigid and likely based on older Waterfall development methodologies that require extensive upfront design. The Waterfall methodology follows a sequential development path that is not flexible to changes in the development process. Your bank has a complex and hierarchical structure, with a culture that does not promote ongoing communication, collaboration, or openness to change. |
For many banks, the Waterfall development approach is still relevant due to the highly regulated nature of the industry and its products/services. Agile can be used in certain areas of your bank in conjunction with Waterfall if:
Assess your bank's suitability for Agile implementation using Info-Tech's Scaled Agile Readiness Assessment Tool. |
Info-Tech Insight
While Agile is very well suited to many dynamic and fast-moving industries, it isn't ideally suited to banking. The size, complexity, and highly regulated nature of banking still requires many banks to use Waterfall. However, banks are increasingly adopting a hybrid approach that uses Waterfall in some areas and Agile in others. The key is understanding where each methodology works best.
Agile was developed to improve speed
Agile helps developers keep up with changing demand in a fast-paced environment
| Attribute | Waterfall | Agile |
| Inception | 1950 | 2001 |
| Roots | Infrastructure and engineering | Software development |
| Client interaction | Minimal | Encouraged |
| Founding artifact | Managing the Development of Large Software Systems by Winston Royce | The Agile Manifesto |
| Implementation frameworks | AgileFall, Sashimi, Incremental Waterfall, Wagile | Scrum, Kanban, Lean, XP, Crystal, FDD, DSDM |
| Preferred by | Banks, governments, insurance companies, large teams | Startups, small teams, SaaS products, small companies |
| Highest priority | Deliver a product that matches initial requirements | Continuously deliver working software to the client |
| Benefits | Enables organizations to do extensive, upfront estimation and planning | Enables teams to rapidly respond to changing requirements |
| Drawbacks | Lack of customer involvement and an overwhelming amount of upfront documentation | Software delivery timelines can be difficult to estimate if requirements frequently change |
Source: TheServerSide, 2022
Info-Tech Insight
Each methodology still has a place in the market. A combination of Agile/Waterfall methodologies is increasingly common.
Agile, as a concept, has become a way of working
AI advancements will further increase the speed to market as more business functions become Agile
The Agile Manifesto was published in 2001 and was created as a response to the prevailing software methodology of the time, which was the Waterfall method.
The Agile Manifesto advanced four core concepts that contrasted with the Waterfall method:1
- Individuals and interactions over processes and tools.
- Working software over comprehensive documentation.
- Customer collaboration over contract negotiation.
- Responding to change over following a plan.
Agile has evolved into something greater than just a software methodology. It has become a management and organizational design methodology that has grown in popularity.
Organizations in rapidly changing and competitive markets are adopting Agile. Hierarchy, process, and rigidity are being replaced by teams, self-organization, and adaptability.
1 InfoWorld, 2022
There is an increasing rate of Agile adoption due to the focus on customer centricity and enabling the rapid development of highly focused new products and services.
Agile has caught up to Waterfall
Across all industries, Agile and Waterfall are about equal as the primary software development approach
Over two decades, Agile has gained ground on Waterfall as the primary methodology

Agile is being combined with other methodologies

Source: Project Management Institute, 2017
Info-Tech Insight
Agile was launched during the dot-com boom. The acceleration of digital transformation through the COVID-19 pandemic has increased the need for Agile methodologies.
Part of Agile's popularity is its alignment with the speed of bank modernization
Employees, infrastructure, data, and development have adopted Agile principles
As banks modernize, they are hiring many new employees. The skills that banks need from their new employees are most often found in organizations outside of banking, where Agile has seen broad adoption. As technology leadership and talent move around, Agile tends to spread into new areas. Banks are among the groups feeling the influence of Agile.
Banks are modernizing their infrastructure and many of the methods align with, or are based on, Agile. The evolution of banks' hardware and software infrastructure have resulted in rigid and complex systems. New market and customer expectations have made legacy software/hardware less relevant. As banks focus on their customers and the need for rapid innovation, Agile's alignment with these elements makes it an appealing approach.
Modern development, data, and technology approaches have evolved out of Agile. As banks modernize their technology, many need to hire talent for new capabilities such as integration skills, microservice development, and data science. These professionals often use Agile methods and tend to want to continue to work within that methodology.
Many banks have come under pressure from fintechs, neobanks, and more agile competitors. Banks believe Agile will help them to compete more effectively.
Waterfall remains relevant to many banks due to complex requirements
Complexity is a key determinant of methodology
Banking products and services are complex. Unlike many other businesses, banks have many levels of technology connections as well as risks that don't typically exist elsewhere. As a result, their products and services require a high degree of planning and design before they are developed and launched.
Regulatory requirements are unique. The banking industry is subject to regulatory scrutiny that requires products/services to be compliant at the time of launch. This challenges a fundamental principle of Agile practices.
There are extensive legal requirements that banks must comply with. Banking is an essential product/service. As a result, it is subject to intense legal compliance that must be designed and executed before the product/service is launched.
Security and privacy requirements are a primary consideration. As a result of the sensitive nature of banking, security and privacy are essential components that must be assured from the outset.
The highly planned and structured nature of Waterfall allows banks to design and orchestrate their products to meet strict legal, regulatory, compliance, security, and privacy requirements before the actual development process begins.
Market forces are leading banks to a hybrid approach with Agile
Digital transformation is reshaping the competitive dynamics of banking
Rapidly escalating competitive dynamics. The banking industry is experiencing intense and accelerating levels of competition and modernization. Both bank and non-bank competitors are using digital product/service innovations to compete with large traditional banks.
Product/service innovation has become essential for survival. Competition is also elevating the need for banks to create new products, services, and customer journeys. Banks have not been strong on innovation. They relied on legal and regulatory barriers to protect their business; however, technology has changed the complex forces in banking. Non-bank competitors with leading-edge infrastructure and enormous amounts of customer data have begun to out-innovate banks, forcing them to respond.
Technology is reshaping how banks operate. Historically, banking required significant investments in technology. However, composable infrastructure using APIs/microservices, advanced vendor capabilities, and next-generation technology such as AI have significantly reduced technology barriers in banking. Banks are now at a disadvantage, compared with their startup competitors, because of their legacy infrastructure and software.
Download the Mainframe Modernization for Retail Banking Report
Current hardware and software development methodologies are not effective in a digitally transforming competitive market.
Agile is driving financial performance
Banks cannot ignore the financial benefits of integrating Agile into development
Top performing organizations are using Agile

More than half of top performers (80% or more of projects being completed on time/budget, meet original goals and business intent, and have high benefits realization) are using Agile
Fewer bottom performing organizations use Agile
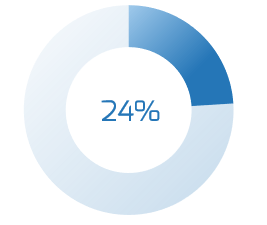
Only one-quarter of bottom performers (60% or less of projects being completed on time/budget, don't meet original goals and business intent, and have low benefits realization) are using Agile
Source: Project Management Institute, 2017
Info-Tech Insight
Accelerating competition in retail banking requires all banks to perform at optimal level, and Agile is another tool to achieve this outcome.
Banks must be selective in how they implement Agile
Agile aligns with modernization efforts
As banks modernize, they are hiring many new employees. The skills that banks need from their new employees are most often found in organizations outside of banking, where Agile has seen very broad adoption. As technology leadership and talent move around, Agile tends to spread into new areas, and banks are among the groups feeling the influence of Agile.
Banks are modernizing their infrastructure, and many of the methods align with, or are based on, Agile. The evolution of banks' hardware and software infrastructure has resulted in rigid and complex systems. New market and customer expectations have made legacy software/hardware less relevant. As banks focus on their customers and the need for rapid innovation, Agile's alignment with these elements makes it an appealing approach.
Modern development, data, and technology approaches have evolved out of Agile. As banks modernize their technology, many need to hire talent for new capabilities such as integration skills, microservice development, and data science. These professionals often use Agile methods and tend to want to continue to work within that methodology.
Download the API Management in Retail Banking report
Many banks have come under pressure from fintechs, neobanks, and more Agile traditional competitors. Banks believe Agile will help them to compete more effectively.
Banks are combining Waterfall's sequential process and Agile's iterative approach

Source: Roadmap for Agile Transformation, Info-Tech Research Group
Info-Tech Insight
In complex areas, likely affecting core services, the highly considered and planned nature of Waterfall works best. Non-core areas are better suited to sprint-style rapid/iterative innovation.
Adopt a hybrid approach to software development
Find the best of both worlds
There are 18 core elements to the current Scaled Agile Framework enterprise (SAFe). Some elements are appropriate for adoption in a bank, while others present special challenges.
Agile implementation will likely be dependent on the size of the bank. Smaller banks that outsource a considerable amount of their technology/infrastructure will realize different benefits than very large banks that have custom-developed a large majority of their infrastructure and software.
The maturity of the bank will also impact the applicability and relevance of Agile. Large scale Agile adoption requires an organization-wide commitment. Communication and collaboration, reduced hierarchy, and distributed authority will be difficult for many banks to adopt.
In most banks, a hybrid approach to Agile will work best. Blind implementation of the full SAFe may produce disastrous results for the bank and its employees. Many adopters of SAFe criticize other organizations for implementing only certain aspects of SAFe, but the majority of the banking industry is not well suited to a full implementation. Find your best hybrid approach.
Non-core banking activities are usually well suited to Agile methods.
Finding your hybrid approach
Consider the guidance on the following slides to determine where Agile best fits in your organization.
The reference architecture can be used to map Agile suitability
Agile alignment can be mapped from poor to good
Good Fit
- Low levels of legal, regulatory, privacy and security requirements.
- Technology is not part of a large monolith/have any dependencies.
- There is good cultural alignment or openness to intensive communication/collaboration.
Close Consideration Required
- The underlying Agile principles have relevance and alignment, but not perfect alignment.
- Care must be taken in these areas to modify Agile methods to suit the needs.
- Each bank's situation will be unique, and the modifications will also be unique.
Potentially Poor Fit
- The core Agile principle is problematic to the essential requirements of a bank.
- The technology, culture, legal, regulatory, privacy, and security requirements conflict.
- Banks must proceed with considerable caution if they decide to use Agile principles in these areas.
Download the Retail Banking Industry Business Reference Architecture
Agile's relevance and suitability can vary across a bank. A heatmap can help to avoid unsuitable use and accelerate positive outcomes.
Example Agile suitability heatmap

The retail banking value stream and business capabilities have different levels of suitability for Agile use.
Your bank can assess the Agile element alignment
The SAFe Framework has 18 core elements across 6 categories

Source: "SAFe 6.0 Framework," Scaled Agile, Inc.
The Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe) version 6.0 is the most current version of Agile. It can be used to assess the suitability of Agile elements across your bank.
Agile is well suited to bank learning and innovation
Each bank has unique circumstances to consider
There are five Agile elements that align well with use in retail banks.
Agile principles are either in use in retail banking or can advance the future goals of many retail banks.

There are elements in SAFe where there is good alignment with banking and where implementation should not be overly challenging.
Agile helps banks respond to change
| Agile Element | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Customer Centricity & Design Thinking |
Almost every bank has customer centricity within its top objectives. Before the onset of rapidly increasing competition, many banks created products that focused primarily on the bank. This era ended some time ago as new neobanks and non-financial competitors capitalized on banks' lack of customer centricity to gain early successes. Agile's core focus is to maximize customer centricity by organizing the bank's resources and effort to achieve this goal. Banks' focus has shifted outward. |
| Built-in Quality |
The requirements in banking are very high. Regulatory, legal, security, and privacy requirements demand compliance from the inception of any new products and services. Upfront planning and design are essential. Banks have already implemented built-in quality concepts throughout their business. To avoid potential reputational risk, banks must ensure this continues to be a central focus. Extending these concepts to new areas is essential. Built-in quality concepts can also be applied to nonessential areas of the banking business. Such areas include customer engagement and satisfaction, which help banks to design and build their products well from inception. |
| Learning Organization |
Banking is in the middle of a massive transformation. Across banks, there is a need for new skills and learning in order to transform and adapt to new market conditions. T-shaped employees help drive value. Employees who acquire broad-based skills but also have a deep specialization are referred to as T-shaped employees. This type of employee knowledge is valuable to a bank going through rapid change. Work is increasingly team-based. Creating cross-functional teams is an effective way to facilitate rapid change within banks. These teams enable the rapid sharing of diverse knowledge, help develop T-shaped employees, and help to achieve the goal of becoming a learning organization. |
Agile supports an innovative ecosystem
| Agile Element | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Innovation Culture |
Running a bank in a traditional way can have dire consequences. The option to continue operating your bank as you have in the past is likely to lead to significant decline in business over time. Innovation and transformation have become imperative. Banks must encourage their employees to explore innovative ideas. Employees should be viewed as a key source of innovation; they deal with the customers and run the processes that power your bank. Innovation from within should be a priority for your bank. Innovation can lead to new products, reduced costs, and happier customers. When innovation is encouraged, your bank will begin to generate ideas that can drive customer satisfaction and engagement through new products and services. Internal processes will also recognize the benefit of innovation through greater automation, new processes and technologies that will reduce your costs and increase your market agility. Innovation must be tied to specific business outcomes. Some banks feel a general need for change to feel like they are doing something. Innovation for the sake of innovation is not productive. |
| Coordinating Trains and Suppliers |
This is an effective way to assemble/build large and complex systems. Reviewing the entire system before it is built is a critical phase in transforming and building the large-scale complex systems that are required in modern banks. Suppliers are increasingly important to building banking ecosystems. The increasing importance of new technologies such as AI/ML creates a greater need for suppliers/vendors in banks. These technological capabilities are almost impossible for all but the largest banks to implement without external vendors. Modern banking infrastructure requires extensive modernization. Composable infrastructure, AI, and fintechs are all critical elements of modern banking. Significant infrastructure upgrades are required to be able to integrate new advanced capabilities. |
Care must be taken in areas involving some processes
Areas of your bank may not align perfectly with Agile
Your bank must evaluate its unique characteristics when determining the suitability of the various components of Agile.
While many of Agile's concepts are appealing, the unique characteristics of banking could make some of them difficult or impossible to implement without major adjustments.

The yellow areas in SAFe represent areas where good alignment and value exists for banks, but some complexity with implementation must be addressed.
Email Infographic
About Info-Tech
Info-Tech Research Group is the world’s fastest-growing information technology research and advisory company, proudly serving over 30,000 IT professionals.
We produce unbiased and highly relevant research to help CIOs and IT leaders make strategic, timely, and well-informed decisions. We partner closely with IT teams to provide everything they need, from actionable tools to analyst guidance, ensuring they deliver measurable results for their organizations.
MEMBER RATING
9.0/10
Overall Impact
After each Info-Tech experience, we ask our members to quantify the real-time savings, monetary impact, and project improvements our research helped them achieve.
What Is a Blueprint?
A blueprint is designed to be a roadmap, containing a methodology and the tools and templates you need to solve your IT problems.
Each blueprint can be accompanied by a Guided Implementation that provides you access to our world-class analysts to help you get through the project.
Talk to an Analyst
Our analyst calls are focused on helping our members use the research we produce, and our experts will guide you to successful project completion.
Book an Analyst Call on This Topic
You can start as early as tomorrow morning. Our analysts will explain the process during your first call.
Get Advice From a Subject Matter Expert
Each call will focus on explaining the material and helping you to plan your project, interpret and analyze the results of each project step, and set the direction for your next project step.
Unlock Sample ResearchAuthor
David Tomljenovic
Unlock Consider Agile for Banking
Get Instant Access
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.
This content is exclusive to members.
Get instant access by signing up!
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.
Search Code: 104801
Last Revised: May 27, 2024
Book an Appointment
IT Research & Advisory Services
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.
Speak With A Representative
Request Content Access
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.








