Cybersecurity Report for Utilities
Safeguard the digital transformation.
Speak With A Representative
Request Content Access
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.
- Embed
- Link
Share
×Speed
×Subtitles
×Your organization is in urgent need of a cybersecurity strategy that can transform with future needs.
You are having difficulty in:
- Gauging the overall risk of the integrated IT, OT, and IIoT cybersecurity ecosystem.
- Developing a strategic plan to protect your organization’s physical assets and brand.
- Understanding the impact on people, processes, and technology.
Our Advice
Critical Insight
Implementation of basic cybersecurity hygiene practices can effectively protect you against easy and low-effort attacks. Adoption of a risk-based approach to secure IT, OT, and IIoT is required to protect you from devastating consequences.
Impact and Result
Info-Tech’s utilities cybersecurity report provides an overview of the cybersecurity landscape that leaders are facing today. It offers key insights and practical recommendations based on industry best practices globally. This report:
- Provides an overview of the utility specific cybersecurity landscape.
- Identifies the impact on People, Process, and Technology as a result of implementing cybersecurity programs.
- Demonstrates how utilities are enhancing their cybersecurity capabilities.
- Proposes recommendations based on best practices from the industry.
Cybersecurity Report for Utilities Research & Tools
1. Utilities Cybersecurity Report – This report provides an overview of the cybersecurity landscape that leaders are facing today.
This trends deep-dive report discusses the risk-based approach to manage utilities’ complex cybersecurity program and highlights the impact of people, process, and technology on building a cybersecurity culture. It offers key insights and practical recommendations based on industry best practices globally.
Speak With A Representative
Request Content Access
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.
Utilities Cybersecurity Report
Safeguard the digital transformation.
Analyst perspective
Digitalization is a double-edged sword. On one hand, it propels automation and enhances control in utilities, driving operational excellence and improving service reliability. On the other hand, it introduces greater risks of cyberattacks due to increasing interconnections across the IT, OT, and IIoT domains.
Security leaders within utilities face a dynamic and complex landscape. Protecting common IT systems and business applications remains important. For many, securing critical infrastructure through developing OT cybersecurity capabilities has become the top priority.
With the increasing adoption of IIoT technologies, utilities are struggling with the sheer volume of devices they now need to protect against sophisticated cyberattacks or breaches. Existing IT cybersecurity experts do not fully understand how OT operates or how to comply with industry-specific regulations and standards. Furthermore, many leaders find themselves reacting to the ever-evolving government policies and regulations.
Cybersecurity has become a prominent topic on the agenda at executive and board meetings. Most of the executive leaders and board members do not have deep knowledge of cybersecurity. To protect the organization from cyberattacks, security leaders are expected to bridge the gap between strategy development and tactical implementation.
Info-Tech's utility cybersecurity report provides an overview of the cybersecurity landscape that leaders are facing today. It offers key insights and practical recommendations based on industry best practices globally.

JING WU
Principal Research Director,
Utilities Research
Info-Tech Research Group
Executive Summary
Your Challenge
Your organization is in urgent need of a cybersecurity strategy that can transform with future needs.
You are having difficulty in:
- Gauging the overall risk of the integrated IT, OT, and IIoT cybersecurity ecosystem.
- Developing a strategic plan to protect your organization's physical assets and brand.
- Understanding the impact on people, processes, and technology.
Common Obstacles
Holistically managing a cybersecurity program among IT, OT, and IIoT systems, often with competing priorities.
Implementing effective cybersecurity strategies with limited funding and resources.
Uncertainties about how and where to start among the complex cybersecurity landscape and evolving regulations.
Reservations about addressing cybersecurity trends, determining how applicable they are to your organization, and what to prioritize.
Info-Tech's Approach
Provide an overview of the utility-specific cybersecurity landscape.
Identify the impact on people, process, and technology as a result of implementing cybersecurity programs.
Demonstrate how utilities are enhancing their cybersecurity capabilities.
Propose recommendations based on best practices from the industry.
Info-Tech Insight
Implementation of basic cybersecurity hygiene practices can effectively protect you against easy and low-effort attacks. Adoption of a risk-based approach to secure IT, OT, and IIoT is required to protect you from devastating consequences.
Integrate cybersecurity in digitalization plans
Digitalization creates new possibilities for utilities
Digitalization enables intelligent utility operations such as optimization of the electricity grid and effective management of natural gas distribution. Technology advancements create opportunities to improve customer services such as alerts about water consumption peaks for potential leakages.
New capabilities bring unique cybersecurity challenges
The cyber threat landscape has changed rapidly. The attack surfaces have enlarged for utilities due to OT connectivity expansion, IT-OT convergence, and growing adoption of cloud and IIoT technologies. Internally, utilities are struggling with antiquated OT systems, a shortage of cybersecurity talent, and a lack of knowledge of cybersecurity regulations. The increasing rate and sophistication of cyberattacks exacerbated the situation.
A comprehensive cybersecurity strategy is a top priority
IT systems have been protected for more than a decade. They have gone through many evolutions through numerous attacks and have reached a certain level of maturity. However, a steep learning curve is anticipated to develop the maturity level for the OT and IoT operating environment. The good news is that OT can fast track by leveraging lessons learned from IT cybersecurity evolution. The bad news is that OT has its unique situations that IT has not gone through. IT-OT collaboration and innovation are required.
560 |
common vulnerabilities and exposures are disclosed with 172 associated products for the first half of 2022. Energy is among the top five sectors affected by the pronounced vulnerabilities. |
(Nozomi Networks, 2022) |
|---|---|---|
45% |
of organizations experienced attacks involving IoT/OT assets according to Ponemon Institute surveys conducted in 2018 and 2019 involving utilities. |
(Industrial Cybersecurity Pulse, 2021) |
217% |
increase in 2021 over 2020 in data compromises in the United States in the Manufacturing and Utilities sector. |
(ITRC, 2022) |
Utility cyberattack risks are diverse
Utilities own and operate a collection of systems, assets, facilities, equipment, and devices that are interacting with the physical world and are interconnected via various communication networks. Beyond the traditional information security domain, a utility's cybersecurity program must have a broader scope to protect against a wide range of targets. Emerging technologies such as IIoT and the antiquated ICS environment create a dynamic landscape. The diverse cybersecurity risk levels and their consequences of cyberattacks add to the complexity. More utilities need to recognize the importance of cybersecurity risk, with only 56% of organizations claiming they use a risk-management approach to assess risks and protect high-risk areas (Siemens, 2020).
![]()
Cyberattacks have significant consequences
Recent cyberattacks against nations' critical infrastructure are wakeup calls for utilities because the consequences of cyberattacks can be devastating. Based on risk assessment of the various attack surfaces, it is imperative for security leaders to weed through technical details and hyperfocus on the broader impact. When discussing cybersecurity impact with leadership and staff, leverage real-time stories besides metrics.
Business, Customer, and Societal Impact

Cybersecurity is about culture, not about checking a box
Developing a cybersecurity culture in utilities takes extra effort. IT and OT teams should stay curious about each other's challenges.
Alex Tremblay, manager of cybersecurity at H2O Power company, shared a well-received practice called A day in a life. IT and OT teams spend the time on job shadowing and experiencing the reality firsthand, instead of just discussing the risks and documenting them.
Don't assume your counterpart does not understand how to manage risks. Build trust through appreciation and understanding.
Walk the extra mile to build the culture
"Cybersecurity is first and foremost about people. We can implement security controls in the systems, but it is the people that use them that are the maker- breaker."
– Ross Lettau,
Principal, Cyber Security, Jacobs
Info-Tech Resources:
Talent shortage is creating a risk
Staff shortage impacts daily operations and opens the utility to cybersecurity risk with three primary consequences related to:
- Systems Misconfigurations
- Lack of Time for Risk Assessment and Management
- Critical Systems Patching Delay
Global cybersecurity workforce supply does not meet the demand. |
65%
increase |
of global workforce supply required to protect critical infrastructure effectively according to estimation done by (ISC)(2). |
|---|---|---|
Total utility cybersecurity job openings from Oct. 2021 to Sept. 2022 in the US. |
4,765 out of 769,736 across all sectors |
Utilities offer less than 1% of opportunities in the highly desired job market. (Data collected on Dec. 12, 2022, Cyberseek) |
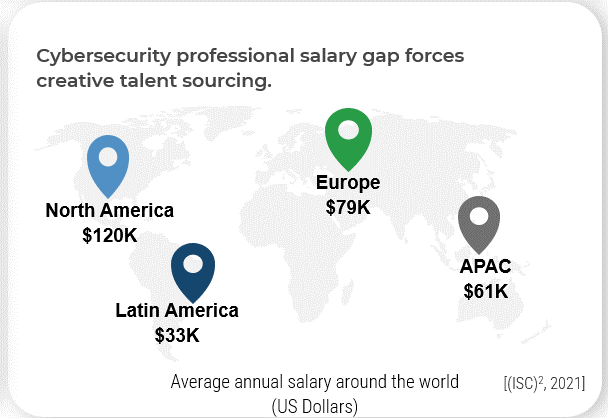
Address the workforce gap
Invest in People
Organizations are focusing on staff development and retention as their top strategy to address the gap. The top five people-centered investments are listed below.
36% |
Training investment |
|---|---|
| 33% | Work flexibility |
| 31% | Certifications |
| 29% | DEI initiatives |
| 28% | Hiring for potentials |
[(ISC)2, 2021] |
|
Info-Tech Resources:
- Cybersecurity Workforce Development Program
- Develop a Security Awareness and Training
Program That Empowers End Users
Offer Multiple Career Pathways
Utility cybersecurity professionals traditionally start out their career in IT or OT engineering. New generations expect to transition to cybersecurity from either education or other related fields.
Leverage Technology
Implementing automation tools to replace manual tasks and highly repeatable processes as well as leveraging cloud services.
Share Resources
The non-competitive nature of the utility industry offers its unique advantage of sharing common cybersecurity personnel. Acquirement through consulting services on an as-needed basis could also be cost effective for smaller utilities.
IT/OT Cross Training
Utilities possess large protected surfaces on the OT space where cross training of the regulations and IT/OT security best practices are mandatory.
[(ISC)2, 2021; NARUC 2021; Fortinet, 2022]
Case Study
Western Power
Providing electric services to more than 2.3 million customers in Western Australia
INDUSTRY: State-Owned Electricity Utility
SOURCE: ICS Security Summit , 2018; Western Power, 2022; Business of InfoSec, 2022
Challenge
Western Power is faced with various challenges to secure its critical infrastructure to be compliant with evolving government regulations.
The convergence of IT and OT increased the interdependencies between traditionally isolated systems. It needed to find effective and efficient ways to secure the ICS to defend against cyberattacks.
Empower modern technologies to transform business operations while not being exposed to increased cybersecurity threats.
Solution
Western Power developed an information and communication technology cybersecurity framework that aligned with updated government regulations.
This new framework enhanced existing corporate security and cybersecurity strategy to create a dedicated operational and technology cybersecurity strategy.
Western Power prioritized investments in safety by highlighting the risks and emphasizing the ROI benefits such as reliability and increased uptime and security.
Results
Western Power has formed a cybersecurity operations team to deliver and improve coreand holistic operational capabilities.
An integrated information and communication technology cybersecurity standard was developed and updated to always align with evolving government regulations.
Western Power has also diversified its hiring strategy to counter the global cybersecurity talent shortages. On-going recruitments are focusing on prescriptive qualifications and experiences such as cybersecurity change management skill sets.
- Embed
- Link
Share
×Speed
×Subtitles
×About Info-Tech
Info-Tech Research Group is the world’s fastest-growing information technology research and advisory company, proudly serving over 30,000 IT professionals.
We produce unbiased and highly relevant research to help CIOs and IT leaders make strategic, timely, and well-informed decisions. We partner closely with IT teams to provide everything they need, from actionable tools to analyst guidance, ensuring they deliver measurable results for their organizations.
What Is a Blueprint?
A blueprint is designed to be a roadmap, containing a methodology and the tools and templates you need to solve your IT problems.
Each blueprint can be accompanied by a Guided Implementation that provides you access to our world-class analysts to help you get through the project.
Talk to an Analyst
Our analyst calls are focused on helping our members use the research we produce, and our experts will guide you to successful project completion.
Book an Analyst Call on This Topic
You can start as early as tomorrow morning. Our analysts will explain the process during your first call.
Get Advice From a Subject Matter Expert
Each call will focus on explaining the material and helping you to plan your project, interpret and analyze the results of each project step, and set the direction for your next project step.
Unlock Sample ResearchAuthor
Jing Wu
Contributors
- Ross Lettau, Principal, Cyber Security, JACOBS
- Robert Dang, Principal Advisory Director, Info-Tech Research Group
- Ida Siahaan, Research Director, Info-Tech Research Group
- Alaisdar Graham, Executive Counselor, Info-Tech Research Group
Unlock Cybersecurity Report for Utilities
Get Instant Access
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.
This content is exclusive to members.
Get instant access by signing up!
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.
Search Code: 100708
Last Revised: February 23, 2023
TAGS:
Cybersecurity, Cyber Security, IT/OT convergence, digital transformation, digital utility, NERC, NERC-CIP, Standards, Frameworks, Regulations, Cyber Attacks, Risk-Based Approach, Critical Infrastructure, IIoT, IoT, DER, ICS, Talent Shortage, Cybersecurity workforce, Governance, Cybersecurity Oversight, Risk Visibility, Supply Chain Security, Electricity, Water, Wastewater, Natural Gas, ISA/IEC – 62433, ISO 27000, NISTBook an Appointment
IT Research & Advisory Services
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.




