Unlock Document and Maintain Your Disaster Recovery Plan
Get Instant Access
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.
Document and Maintain Your Disaster Recovery Plan
Keep your DRP fit, trim, and ready for action.
- Disaster recovery plan (DRP) documentation is often driven by audit or compliance requirements rather than aimed at the team that would need to execute recovery.
- Between day-to-day IT projects and the difficulty of maintaining 300+ page manuals, DRP documentation is not updated and quickly becomes unreliable.
- Inefficient publishing strategies result in your DRP not being accessible during disaster or key staff not knowing where to find the latest version.
Our Advice
Critical Insight
- DR documentation fails when organizations try to boil the ocean with an all-in-one plan aimed at auditors, business leaders, and IT. It’s too long, too hard to maintain, and ends up being little more than shelf-ware.
- Using flowcharts, checklists, and diagrams aimed at an IT audience is more concise and effective in a disaster, quicker to create, and easier to maintain.
- Create your DRP in layers to keep the work manageable. Start with a recovery workflow to ensure a coordinated response, and build out supporting documentation over time.
Impact and Result
- Create visual and concise DR documentation that strips out unnecessary content and is written for an IT audience – the team that would actually be executing the recovery. Your business leaders can take the same approach to create separate business response plans. Don’t mix the two in an all-in-one plan that is not effective for either audience.
- Determine a documentation distribution strategy that supports ease of maintenance and accessibility during a disaster.
- Incorporate DRP maintenance into change management procedures to systematically update and refine the DR documentation. Don’t save up changes for a year-end blitz, which turns document maintenance into an onerous project.
Document and Maintain Your Disaster Recovery Plan Research & Tools
1. Streamline DRP documentation
Start by documenting your recovery workflow. Create supporting documentation in the form of checklists, flowcharts, topology diagrams, and contact lists. Finally, summarize your DR capabilities in a DRP Summary Document for stakeholders and auditors.
2. Select the optimal DRP publishing strategy
Select criteria for assessing DRP tools, and evaluate whether a business continuity management tool, document management solution, wiki site, or manually distributing documentation is best for your DR team.
3. Keep your DRP relevant through maintenance best practices
Learn how to integrate DRP maintenance into core IT processes, and learn what to look for during testing and during annual reviews of your DRP.
4. Appendix: XMPL Case Study
Model your DRP after the XMPL case study disaster recovery plan documentation.
Member Testimonials
After each Info-Tech experience, we ask our members to quantify the real-time savings, monetary impact, and project improvements our research helped them achieve. See our top member experiences for this blueprint and what our clients have to say.
10.0/10
Overall Impact
$13,700
Average $ Saved
14
Average Days Saved
Client
Experience
Impact
$ Saved
Days Saved
Testimonial
Ucla Anderson School of Management
Guided Implementation
10/10
$13,700
14
Best part is validating the approach and process when implementing a new ITDR Program into our operational tempo.
CLDigital
Guided Implementation
10/10
N/A
N/A
Frank listened to my research needs and followed up on how Infotech is helping. The operational resilience research and blueprint is a high priori... Read More
Frank listened to my research needs and followed up on how Infotech is helping. The operational resilience research and blueprint is a high priority for risk and resilience. I hope Infotech prioritizes this important work for the upcoming cycle. Read Less
Document and Maintain Your Disaster Recovery Plan
Keep your DRP fit, trim, and ready for action.
ANALYST PERSPECTIVE
The traditional disaster recovery plan (DRP) “red binder” is dead. It takes too long to create, it’s too hard to maintain, and it’s not usable in a crisis.
“This blueprint outlines the following key tactics to streamline your documentation effort and produce a better result:
- Write for an IT audience and focus on how to recover. You don’t need 30 pages of fluff describing the purpose of the document.
- Use flowcharts, checklists, and diagrams over traditional manuals. This drives documentation that is more concise, easier to maintain, and effective in a crisis.
- Create your DRP in layers to get tangible results faster, starting with a recovery workflow that outlines your DR strategy, and then build out the specific documentation needed to support recovery.”
This project is about DRP documentation after you have clarified your DR strategy; create these necessary inputs first
These artifacts are the cornerstone for any disaster recovery plan.
- Business Impact Analysis
- DR Roles and Responsibilities
- Recovery Workflow
Missing a component? Start here. ➔ Create a Right-Sized Disaster Recovery Plan
This blueprint walks you through building these inputs.
Our approach saves clients on average US$16,825.22. (Clients self-reported an average saving of US$16,869.21 while completing the Create a Right-Sized Disaster Recovery Plan blueprint through advisory calls, guided implementations, or workshops (Info-Tech Research Group, 2017, N=129).)
How this blueprint will help you document your DRP
This Research is Designed For:
- IT managers in charge of disaster recovery planning (DRP) and execution.
- Organizations seeking to optimize their DRP using best-practice methodology.
- Business continuity professionals that are involved with disaster recovery.
This Research Will Help You:
- Divide the process of creating DR documentation into manageable chunks, providing a defined scope for you to work in.
- Identify an appropriate DRP document management and distribution strategy.
- Ensure that DR documentation is up to date and accessible.
This Research Will Also Assist:
- IT managers preparing for a DR audit.
- IT managers looking to incorporate components of DR into an IT operations document.
This Research Will Help Them:
- Follow a structured approach in building DR documentation using best practices.
- Integrate DR into day-to-day IT operations.
Executive summary
Situation
- DR documentation is often driven by audit or compliance requirements, rather than aimed at the team that would need to execute recovery.
- Traditional DRPs are text-heavy, 300+ page manuals that are simply not usable in a crisis.
- Compounding the problem, DR documentation is rarely updated, so it’s just shelf-ware.
Complication
- DRP is often given lower priority as day-to-day IT projects displace DR documentation efforts.
- Inefficient publishing strategies result in your DRP not being accessible during disasters or key staff not knowing where to find the latest version.
- Organizations that create traditional DRPs end up with massive manuals that are difficult to maintain, so they quickly become unreliable.
Resolution
- Create visual and concise DR documentation that strips out unnecessary content and is written for an IT audience – the team that would actually be executing the recovery. Your business leaders can take the same approach to create separate business response plans – don’t mix the two into an all-in-one plan that is not effective for either audience.
- Determine a documentation distribution strategy that supports ease of maintenance and accessibility during a disaster.
- Incorporate DRP maintenance into change management and project intake procedures to systematically update and refine the DR documentation. Don’t save up changes for a year-end blitz, which turns document maintenance into an onerous project.
Info-Tech Insight
- DR documentation fails when organizations try to boil the ocean with an all-in-one plan aimed at auditors, business leaders, and IT. It’s too long, too hard to maintain, and ends up being little more than shelf-ware.
- Using flowcharts, checklists, and diagrams aimed at an IT audience is more concise and effective in a disaster, quicker to create, and easier to maintain.
- Create your DRP in layers to keep the work manageable. Start with a recovery workflow to ensure a coordinated response, and build out supporting documentation over time.
An effective DRP that mitigates a wide range of potential outages is critical to minimizing the impact of downtime
The criticality of having an effective DRP is underestimated.
Cost of Downtime for the Fortune 1000
- Cost of unplanned apps downtime per year: $1.25B to $2.5B
- Cost of critical apps failure per hour: $500,000 to $1M
- Cost of infrastructure failure per hour: $100,000
- 35% reported to have recovered within 12 hours.
- 17% of infrastructure failures took more than 24 hours to recover.
- 13% of application failures took more than 24 hours to recover.
Size of Impact Increasing Across Industries
- The cost of downtime is rising across the board and not just for organizations that traditionally depend on IT (e.g. e-commerce).
- Downtime cost increase since 2010:
- Hospitality: 129% increase
- Transportation: 108% increase
- Media organizations: 104% increase
Potential Lost Revenue

(Adapted from: Rothstein, Philip Jan. Disaster Recovery Testing: Exercising Your Contingency Plan (2007 Edition).)
The impact of downtime increases significantly over time, not just in terms of lost revenue (as illustrated here) but also goodwill/reputation and health/safety. An effective DR solution and overall resiliency that mitigate a wide range of potential outages are critical to minimizing the impact of downtime.
Without an effective DRP, your organization is gambling on being able to define and implement a recovery strategy during a time of crisis. At the very least, this means extended downtime – potentially weeks – and substantial impact.
Only 38% of those with a full or mostly complete DRP believe their DRPs would be effective in a real crisis
Organizations continue to struggle with creating DRPs, let alone making them actionable.
Why are so many living with either an incomplete or ineffective DRP? For the same reasons that IT documentation in general continues to be a pain point:
- It is an outdated model of what documentation should be – the traditional manual with detailed (lengthy) descriptions and procedures.
- Despite the importance of DR, low priority is placed on creating a DRP and the day-to-day SOPs required to support a recovery.
- There is a lack of effective processes for ensuring documentation stays up to date.
 (Source: Info-Tech Research Group, N=165) |
 (Source: Info-Tech Research Group, N=69 (includes only those who indicated DRP is mostly completed or completed)) |
Improve usability and effectiveness with visual-based and more-concise documentation
Choose flowcharts over process guides, checklists over lengthy procedures, and diagrams over descriptions.
If you need a three-inch binder to hold your DRP, imagine having to flip through it to determine next steps during a crisis.
DR documentation needs to be concise, scannable, and quickly understood to be effective. Visual-based documentation meets these requirements, so it’s no surprise that it also leads to higher DR success.
DR success scores are based on:
- Meeting recovery time objectives (RTOs).
- Meeting recovery point objectives (RPOs).
- IT staff’s confidence in their ability to meet RTOs/RPOs.
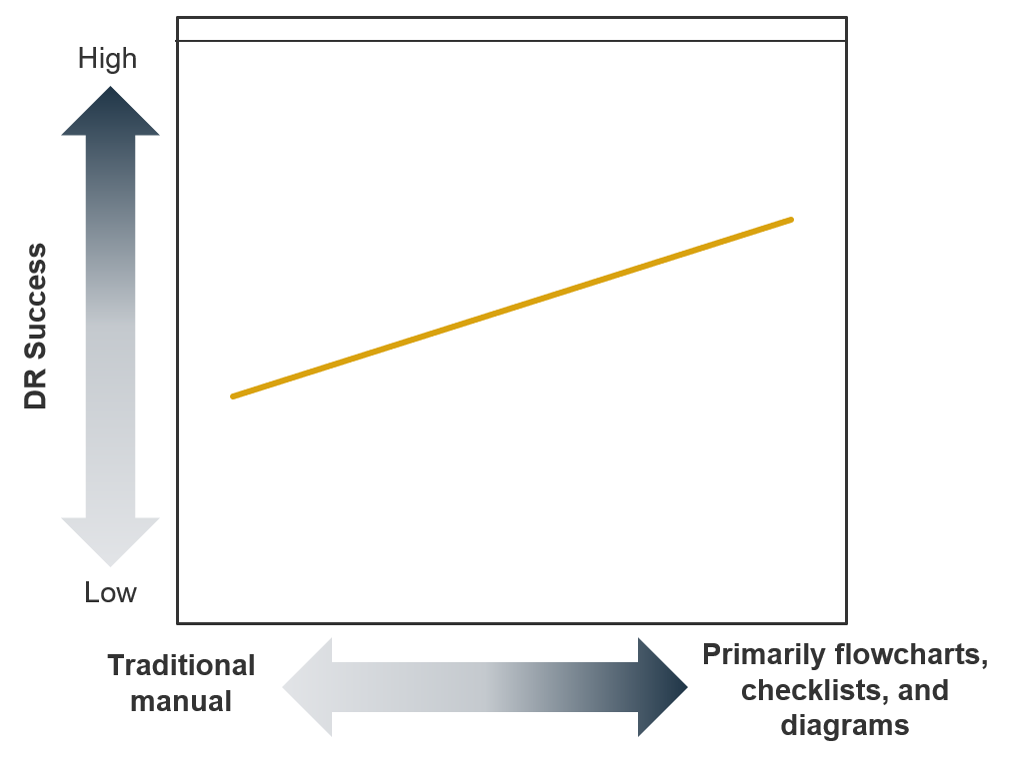 (Source: Info-Tech Research Group, N=95)
(Source: Info-Tech Research Group, N=95)
“Without question, 300-page DRPs are not effective. I mean, auditors love them because of the detail, but give me a 10-page DRP with contact lists, process flows, diagrams, and recovery checklists that are easy to follow.” (Bernard Jones, MBCI, CBCP, CORP, Manager Disaster Recovery/BCP, ActiveHealth Management)
Maintainability is another argument for visual-based, concise documentation
There are two end goals for your DR documentation: effectiveness and maintainability. Without either, you will not have success during a disaster.
| Organizations using a visual-based approach were 30% more likely to find that DR documentation is easy to maintain. | ➔ | “Easy to maintain” leads to a 46% higher rate of DR success. |

|
||
Not only are visual-based disaster recovery plans more effective, but they are also easier to maintain.
Overcome documentation inertia with a tiered model that allows you to eat the elephant one bite at a time
Start with a recovery workflow to at least ensure a coordinated response. Then use that workflow to determine required supporting documentation.
Recovery Workflow: Starting the project with overly detailed documentation can slow down the entire process. Overcome planning inertia by starting with high-level incident response plans in a flowchart format. For examples and additional information, see XMPL Medical’s Recovery Workflows.
Recovery Procedures (Systems Recovery Playbook): For each step in the high-level flowchart, create recovery procedures where necessary using additional flowcharts, checklists, and diagrams as appropriate. Leverage Info-Tech’s Systems Recovery Playbook example as a starting point.
Additional Reference Documentation: Reference existing IT documentation, such as network diagrams and configuration documents, as well as more detailed step-by-step procedures where necessary (e.g. vendor documentation), particularly where needed to support alternate recovery staff who may not be as well versed as the primary system owners.
Info-Tech Insight
Organizations that use flowcharts, checklist, and diagrams over traditional, dense DRP manuals are far more likely to meet their RTOs/RPOs because their documentation is more usable and easier to maintain.
Use a DRP summary document to satisfy executives, auditors, and clients
Stakeholders don’t have time to sift through a pile of paper. Summarize your overall continuity capabilities in one, easy-to-read place.
DRP Summary Document
- Summarize BIA results
- Summarize DR strategy (including DR sites)
- Summarize backup strategy
- Summarize testing and maintenance plans
Follow Info-Tech’s methodology to make DRP documentation efficient and effective
Phases |
Phase 1: Streamline DRP documentation | Phase 2: Select the optimal DRP publishing strategy | Phase 3: Keep your DRP relevant through maintenance best practices | |||
Phases |
1.1 |
Start with a recovery workflow |
2.1 |
Decide on a publishing strategy |
3.1 |
Incorporate DRP maintenance into core IT processes |
1.2 |
Create supporting DRP documentation |
3.2 |
Conduct an annual focused review | |||
1.3 |
Write the DRP Summary | |||||
Tools and Templates |
End-to-End Sample DRP | DRP Publishing Evaluation Tool | Project In-take/Request Form
Change Management Checklist |
|||
Follow XMPL Medical’s journey through DR documentation
CASE STUDY
Industry Healthcare
Source Created by amalgamating data from Info-Tech’s client base
Streamline your documentation and maintenance process by following the approach outlined in XMPL Medical’s journey to an end-to-end DRP.
Outline of the Disaster Recovery Plan
XMPL’s disaster recovery plan includes its business impact analysis and a subset of tier 1 and tier 2 patient care applications.
Its DRP includes incident response flowcharts, system recovery checklists, and a communication plan. Its DRP also references IT operations documentation (e.g. asset management documents, system specs, and system configuration docs), but this material is not published with the example documentation.
Resulting Disaster Recovery Plan
XMPL’s DRP includes actionable documents in the form of high-level disaster response plan flowcharts and system recovery checklists. During an incident, the DR team is able to clearly see the items for which they are responsible.
Disaster Recovery Plan
- Recovery Workflow
- Business Impact Analysis
- DRP Summary
- System Recovery Checklists
- Communication, Assessment, and Disaster Declaration Plan
Info-Tech Best Practice
XMPL Medical’s disaster recovery plan illustrates an effective DRP. Model your end-to-end disaster recovery plan after XMPL’s completed templates. The specific data points will differ from organization to organization, but the structure of each document will be similar.
Model your disaster recovery documentation off of our example
CASE STUDY
Industry Healthcare
Source Created by amalgamating data from Info-Tech’s client base
Recovery Workflow:
- Recovery Workflows (PDF, VSDX)
Recovery Procedures (Systems Recovery Playbook):
- DR Notification, Assessment, and Disaster Declaration Plan
- Systems Recovery Playbook
- Network Topology Diagrams
Additional Reference Documentation:
- DRP Workbook
- Business Impact Analysis
- DRP Summary Document
Use Info-Tech’s DRP Maturity Scorecard to evaluate your progress
Info-Tech offers various levels of support to best suit your needs
DIY Toolkit |
Guided Implementation |
Workshop |
Consulting |
| "Our team has already made this critical project a priority, and we have the time and capability, but some guidance along the way would be helpful." | "Our team knows that we need to fix a process, but we need assistance to determine where to focus. Some check-ins along the way would help keep us on track." | "We need to hit the ground running and get this project kicked off immediately. Our team has the ability to take this over once we get a framework and strategy in place." | "Our team does not have the time or the knowledge to take this project on. We need assistance through the entirety of this project." |
Diagnostics and consistent frameworks used throughout all four options
Document and Maintain Your Disaster Recovery Plan – Project Overview
| 1. Streamline DRP Documentation | 2. Select the Optimal DRP Publishing Strategy | 3. Keep Your DRP Relevant | |
|---|---|---|---|
 Best-Practice Toolkit |
1.1 Start with a recovery workflow 1.2 Create supporting DRP documentation 1.3 Write the DRP summary |
2.1 Create Committee Profiles |
3.1 Build Governance Structure Map 3.2 Create Committee Profiles |
| Guided Implementations |
|
|
|

Onsite Workshop |
Module 1:
Streamline DRP documentation |
Module 2:
Select the optimal DRP publishing strategy |
Module 3:
Learn best practices for keeping your DRP relevant |
Phase 1 Outcome:
|
Phase 2 Outcome:
|
Phase 3 Outcome:
|
Workshop Overview 
Contact your account representative or email Workshops@InfoTech.com for more information.
| Workshop Day 1 | Workshop Day 2 | Workshop Day 3 | Workshop Day 4 | Workshop Day 5 Info-Tech Analysts Finalize Deliverables |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activities |
Assess DRP Maturity and Review Current Capabilities0.1 Assess current DRP maturity through Info-Tech’s Maturity Scorecard. 0.2 Identify the IT systems that support mission-critical business activities, and select 2 or 3 key applications to be the focus of the workshop. 0.3 Identify current recovery strategies for selected applications. 0.4 Identify current DR challenges for selected applications. |
Document Your Recovery Workflow1.1 Create a recovery workflow: review tabletop planning, walk through DR scenarios, identify DR gaps, and determine how to fill them. |
Create Supporting Documentation1.2 Create supporting DRP documentation. 1.3 Write the DRP summary. |
Establish a DRP Publishing, Management, and Maintenance Strategy2.1 Decide on a publishing strategy. 3.1 Incorporate DRP maintenance into core IT. 3.2 Considerations for reviewing your DRP regularly. |
|
| Deliverables |
|
|
|
|
Workshop Goal: Learn how to document and maintain your DRP.
Use these icons to help direct you as you navigate this research
Use these icons to help guide you through each step of the blueprint and direct you to content related to the recommended activities.

This icon denotes a slide where a supporting Info-Tech tool or template will help you perform the activity or step associated with the slide. Refer to the supporting tool or template to get the best results and proceed to the next step of the project.

This icon denotes a slide with an associated activity. The activity can be performed either as part of your project or with the support of Info-Tech team members, who will come onsite to facilitate a workshop for your organization.
Phase 1: Streamline DRP Documentation
Step 1.1: Start with a recovery workflow
PHASE 1 |
PHASE 2 |
PHASE 3 |
|||
| 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 2.1 | 3.1 | 3.2 |
| Start with a Recovery Workflow | Create Supporting Documentation | Write the DRP Summary | Select DRP Publishing Strategy | Integrate into Core IT Processes | Conduct an Annual Focused Review |
This step will walk you through the following activities:
- Review a model DRP.
- Review your recovery workflow.
- Identify documentation required to support the recovery workflow.
This step involves the following participants:
- DRP Owner
- System SMEs
- Alternate DR Personnel
Outcomes of this step
- Understanding the visual-based, concise approach to DR documentation.
- Creating a recovery workflow that provides a roadmap for coordinating incident response and identifying required supporting documentation.
Info-Tech Insights
A DRP is a collection of procedures and supporting documents that allow an organization to recover its IT services to minimize system downtime for the business.

About Info-Tech
Info-Tech Research Group is the world’s fastest-growing information technology research and advisory company, proudly serving over 30,000 IT professionals.
We produce unbiased and highly relevant research to help CIOs and IT leaders make strategic, timely, and well-informed decisions. We partner closely with IT teams to provide everything they need, from actionable tools to analyst guidance, ensuring they deliver measurable results for their organizations.
MEMBER RATING
10.0/10
Overall Impact
$13,700
Average $ Saved
14
Average Days Saved
After each Info-Tech experience, we ask our members to quantify the real-time savings, monetary impact, and project improvements our research helped them achieve.
What Is a Blueprint?
A blueprint is designed to be a roadmap, containing a methodology and the tools and templates you need to solve your IT problems.
Each blueprint can be accompanied by a Guided Implementation that provides you access to our world-class analysts to help you get through the project.
Need Extra Help?
Speak With An Analyst
Get the help you need in this 3-phase advisory process. You'll receive 10 touchpoints with our researchers, all included in your membership.
Guided Implementation 1: Streamline DRP documentation
- Call 1: Review Info-Tech’s approach to DRP documentation.
- Call 2: Create a high-level recovery workflow.
- Call 3: Create supporting DRP documentation.
- Call 4: Write the DRP summary.
Guided Implementation 2: Select the optimal DRP publishing strategy
- Call 1: Identify criteria for selecting a DRP publishing strategy.
- Call 2: Select a DRP publishing strategy.
- Call 3: Optional: Select requirements for a BCM tool and issue an RFP.
- Call 4: Optional: Review responses to RFP.
Guided Implementation 3: Keep your DRP relevant through maintenance best practices
- Call 1: Learn best practices for integrating DRP maintenance into day-to-day IT processes.
- Call 2: Learn best practices for DRP-focused reviews.
Authors
Frank Trovato
Ken Weston
Related Content: DR and Business Continuity
Unlock Document and Maintain Your Disaster Recovery Plan
Get Instant Access
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.
This content is exclusive to members.
Get instant access by signing up!
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.
Search Code: 17591
Last Revised: September 29, 2017
Book an Appointment
IT Research & Advisory Services
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.
Speak With A Representative
Request Content Access
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.
 Create a Right-Sized Disaster Recovery Plan
Create a Right-Sized Disaster Recovery Plan
 Develop a Business Continuity Plan
Develop a Business Continuity Plan
 Mitigate the Risk of Cloud Downtime and Data Loss
Mitigate the Risk of Cloud Downtime and Data Loss
 Ensure DRP and BCP Compliance With Industry Standards
Ensure DRP and BCP Compliance With Industry Standards
 Select the Optimal Disaster Recovery Deployment Model
Select the Optimal Disaster Recovery Deployment Model
 Take a Realistic Approach to Disaster Recovery Testing
Take a Realistic Approach to Disaster Recovery Testing
 Implement Crisis Management Best Practices
Implement Crisis Management Best Practices
 Create Visual SOP Documents that Drive Process Optimization, Not Just Peace of Mind
Create Visual SOP Documents that Drive Process Optimization, Not Just Peace of Mind
 Document and Maintain Your Disaster Recovery Plan
Document and Maintain Your Disaster Recovery Plan
 10 Secrets for Successful Disaster Recovery in the Cloud
10 Secrets for Successful Disaster Recovery in the Cloud
 Develop a COVID-19 Pandemic Response Plan
Develop a COVID-19 Pandemic Response Plan
 Reinforce End-User Security Awareness During Your COVID-19 Response
Reinforce End-User Security Awareness During Your COVID-19 Response
 Execute an Emergency Remote Work Plan
Execute an Emergency Remote Work Plan
 Prepare Your Organization to Successfully Embrace the “New Normal”
Prepare Your Organization to Successfully Embrace the “New Normal”
 Tech Trend Update: If Contact Tracing Then Distributed Trust
Tech Trend Update: If Contact Tracing Then Distributed Trust
 Microsoft Teams Cookbook
Microsoft Teams Cookbook
 Business Continuity Management Software Selection Guide
Business Continuity Management Software Selection Guide
 Maintain Continuity in a Power Outage
Maintain Continuity in a Power Outage






