Unlock Integrate IT Risk Into Enterprise Risk
Get Instant Access
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.
Integrate IT Risk Into Enterprise Risk
Don’t fear IT risks, integrate them.
Speed
×- IT risks, when considered, are identified and classified separately from the enterprise-wide perspective.
- IT is expected to own risks over which they have no authority or oversight.
- Poor behaviors, such as only considering IT risks when conducting compliance or project due diligence, have been normalized.
Our Advice
Critical Insight
- Stop avoiding risk – integrate it. This provides a holistic view of uncertainty for the organization to drive innovative new approaches to optimize the organization’s ability to respond to risk.
Impact and Result
- Understand gaps in the organization’s current approach to risk management practices.
- Establish a standardized approach for how IT risks impact the enterprise as a whole.
- Drive a risk-aware organization toward innovation and consider alternative options for how to move forward.
- Integrate IT risks into the foundational risk practice.
Integrate IT Risk Into Enterprise Risk Research & Tools
Integrated Risk Management Capstone – A framework for how IT risks can be integrated into your organization’s enterprise risk management program to enable strategic risk-informed decisions.
This is a capstone blueprint highlighting the benefits of an integrated risk management program that uses risk information and data to inform strategic decision making. Throughout this research you will gain insight into the five core elements of integrating risk through assessing, governing, defining the program, defining the process, and implementing.
Member Testimonials
After each Info-Tech experience, we ask our members to quantify the real-time savings, monetary impact, and project improvements our research helped them achieve. See our top member experiences for this blueprint and what our clients have to say.
9.7/10
Overall Impact
$12,599
Average $ Saved
6
Average Days Saved
Client
Experience
Impact
$ Saved
Days Saved
Testimonial
PLUXEE BENEFÍCIOS BRASIL S.A.
Guided Implementation
10/10
N/A
10
Rhode Island Medical Imaging
Guided Implementation
9/10
N/A
N/A
At this stage of the discussion, it is difficult to say how much time and effort this will save us. However, in our hour discussing the issue it is... Read More
At this stage of the discussion, it is difficult to say how much time and effort this will save us. However, in our hour discussing the issue it is clear Valence's experience will be very useful. He provided comprehensive responses to my questions and clearly has the experience to help us through a guided implementation. Look forward to working with him. Read Less
Leprino Foods Company
Guided Implementation
10/10
$12,599
2
Donna was very knowledgeable about the market and had real world experience with Workforce and Payroll.
Integrate IT Risk Into Enterprise Risk
Don’t fear IT risks, integrate them.
EXECUTIVE BRIEF
Analyst Perspective
Having siloed risks is risky business for any enterprise.

Valence Howden Principal Research Director, CIO Practice |

Petar Hristov Research Director, Security, Privacy, Risk & Compliance |

Ian Mulholland Research Director, Security, Risk & Compliance |

Brittany Lutes Senior Research Analyst, CIO Practice |

Ibrahim Abdel-Kader Research Analyst, CIO Practice |
Every organization has a threshold for risk that should not be exceeded, whether that threshold is defined or not.
In the age of digital, information and technology will undoubtedly continue to expand beyond the confines of the IT department. As such, different areas of the organization cannot address these risks in silos. A siloed approach will produce different ways of identifying, assessing, responding to, and reporting on risk events. Integrated risk management is about embedding IT uncertainty to inform good decision making across the organization.
When risk is integrated into the organization's enterprise risk management program, it enables a single view of all risks and the potential impact of each risk event. More importantly, it provides a consistent view of the risk event in relation to uncertainty that might have once been seemingly unrelated to IT.
And all this can be achieved while remaining within the enterprise’s clearly defined risk appetite.
Executive Summary
Your Challenge
Most organizations fail to integrate IT risks into enterprise risks:
- IT risks, when considered, are identified and classified separately from the enterprise-wide perspective.
- IT is expected to own risks over which they have no authority or oversight.
- Poor behaviors, such as only considering IT risks when conducting compliance or project due diligence, have been normalized.
Common Obstacles
IT leaders have to overcome these obstacles when it comes to integrating risk:
- Making business leaders aware of, involved in, and able to respond to all enterprise risks.
- A lack of data or information being used to support a holistic risk management process.
- A low level of enterprise risk maturity.
- A lack of risk management capabilities.
Info-Tech’s Approach
By leveraging the Info-Tech Integrated Risk approach, your business can better address and embed risk by:
- Understanding gaps in the organization’s current approach to risk management practices.
- Establishing a standardized approach for how IT risks impact the enterprise as a whole.
- Driving a risk-aware organization toward innovation and considering alternative options for how to move forward.
- Helping integrate IT risks into the foundational risk practice.
Info-Tech Insight
Stop avoiding risk – integrate it. This provides a holistic view of uncertainty for the organization to drive innovative new approaches to optimize its ability to respond to risk.
What is integrated risk management?
- Integrated risk management is the process of ensuring all forms of risk information, including information and technology, are considered and included in the enterprise’s risk management strategy.
- It removes the siloed approach to classifying risks related to specific departments or areas of the organization, recognizing that each of those risks is a threat to the overarching enterprise.
- Aggregating the different threats or uncertainty that might exist within an organization allows for informed decisions to be made that align to strategic goals and continue to drive value back to the business.
- By holistically considering the different risks, the organization can make informed decisions on the best course of action that will reduce any negative impacts associated with the uncertainty and increase the overall value.
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM)
- IT
- Security
- Digital
- Vendor/Third Party
- Other
Enterprise risk management is the practice of identifying and addressing risks to your organization and using risk information to drive better decisions and better opportunities.
IT risk is enterprise risk

|
IT risks have a direct and often aggregated impact on enterprise risks and opportunities in the same way other business risks can. This relationship must be understood and addressed through integrated risk management to ensure a consistent approach to risk. |
Your challenge
Embedding IT risks into the enterprise risk management program is challenging because:
- Most organizations classify risks based on the departments or areas of the business where the uncertainty is likely to happen.
- Unnecessary expectations are placed on the IT department to own risks over which they have no authority or oversight.
- Risks are often only identified when conducting due diligence for a project or ensuring compliance with regulations and standards.
Risk-mature organizations have a unique benefit in that they often have established an overarching governance framework and embedded risk awareness into the culture.
35% — Only 35% of organizations had embraced ERM in 2020. (Source: AICPA and NC State Poole College of Management)
12% — Only 12% of organizations are leveraging risk as a tool to their strategic advantage. (Source: AICPA and NC State Poole College of Management)
Common obstacles
These barriers make integrating IT risks difficult to address for many organizations:
- IT risks are not seen as enterprise risks.
- The organization’s culture toward risk is not defined.
- The organization’s appetite and threshold for risk are not defined.
- Each area of the organization has a different method of identifying, assessing, and responding to risk events.
- Access to reliable and informative data to support risk management is difficult to obtain.
- Leadership does not see the business value of integrating risk into a single management program.
- The organization’s attitudes and behaviors toward risk contradict the desired and defined risk culture.
- Skills, training, and resources to support risk management are lacking, let alone those to support integrated risk management.
Integrating risks has its challenges
62% — Accessing and disseminating information is the main challenge for 62% of organizations maturing their organizational risk management. (Source: OECD)
20-28% — Organizations with access to machine learning and analytics to address future risk events have 20 to 28% more satisfaction. (Source: Accenture)
Integrate Risk and Use It to Your Advantage
Accelerate and optimize your organization by leveraging meaningful risk data to make intelligent enterprise risk decisions.
Risk management is more than checking an audit box or demonstrating project due diligence.
Risk Drivers
|
Only 7% of organizations are in a “leading” or “aspirational” level of risk maturity. (OECD, 2021) | 63% of organizations struggle when it comes to defining their appetite toward strategy related risks. (“Global Risk Management Survey,” Deloitte, 2021) | Late adopters of risk management were 70% more likely to use instinct over data or facts to inform an efficient process. (Clear Risk, 2020) | 55% of organizations have little to no training on ERM to properly implement such practices. (AICPA, NC State Poole College of Management, 2021) | |
| 1. Assess Enterprise Risk Maturity | 3. Build a Risk Management Program Plan | 4. Establish Risk Management Processes | 5. Implement a Risk Management Program | ||
| 2. Determine Authority with Governance
Unfortunately, less than 50% of those in risk focused roles are also in a governance role where they have the authority to provide risk oversight. (Governance Institute of Australia, 2020) |
|||||
| IT can improve the maturity of the organization’s risk governance and help identify risk owners who have authority and accountability.
Governance and related decision making is optimized with integrated and aligned risk data. |

|

ERM incorporates the different types of risk, including IT, security, digital, vendor, and other risk types. The program plan is meant to consider all the major risk types in a unified approach. |

|
Implementation of an integrated risk management program requires ongoing access to risk data by those with decision making authority who can take action. | |
Integrated Risk Mapping — Downside Risk Focus

Integrated Risk Mapping — Downside and Upside Risk
Third-Party Risk Example

Insight Summary
Overarching insight
Stop fearing risk – integrate it. Integration leads to opportunities for organizations to embrace innovation and new digital technologies as well as reducing operational costs and simplifying reporting.
Govern risk strategically
Governance of risk management for information- and technology-related events is often misplaced. Just because it's classified as an IT risk does not mean it shouldn’t be owned by the board or business executive.
Assess risk maturity
Integrating risk requires a baseline of risk maturity at the enterprise level. IT can push integrating risks, but only if the enterprise is willing to adopt the attitudes and behaviors that will drive the integrated risk approach.
Manage risk
It is not a strategic decision to have different areas of the organization manage the risks perceived to be in their department. It’s the easy choice, but not the strategic one.
Implement risk management
Different areas of an enterprise apply risk management processes differently. Determining a single method for identification, assessment, response, and monitoring can ensure successful implementation of enterprise risk management.
Tactical insight
Good risk management will consider both the positives and negatives associated with a risk management program by recognizing both the upside and downside of risk event impact and likelihood.
Integrated risk benefits
IT Benefits
|
Business Benefits
|
Measure the value of integrating risk
-
Reduce Operating Costs
- Organizations can reduce their risk operating costs by 20 to 30% by adopting enterprise-wide digital risk initiatives (McKinsey & Company).
-
Increase Cybersecurity Threat Preparedness
- Increase the organization’s preparedness for cybersecurity threats. 79% of organizations that were impacted by email threats in 2020 were not prepared for the hit (Diligent)
-
Increase Risk Management’s Impact to Drive Strategic Value
- Currently, only 3% of organizations are extensively using risk management to drive their unique competitive advantage, compared to 35% of companies who do not use it at all (AICPA & NC State Poole College of Management).
-
Reduce Lost Productivity for the Enterprise
- Among small businesses, 76% are still not considering purchasing cyberinsurance in 2021, despite the fact that ransomware attacks alone cost Canadian businesses $5.1 billion in productivity in 2020 (Insurance Bureau of Canada, 2021).
“31% of CIO’s expected their role to expand and include risk management responsibilities.” (IDG “2021 State of the CIO,” 2021)
Make integrated risk management sustainable
58%Focus not just on the preventive risk management but also the value-creating opportunities. With 58% of organizations concerned about disruptive technology, it’s an opportunity to take the concern and transform it into innovation. (Accenture) |
70%Invest in tools that have data and analytics features. Currently, “gut feelings” or “experience” inform the risk management decisions for 70% of late adopters. (Clear Risk) |
54%Align to the strategic vision of the board and CEO, given that these two roles account for 54% of the accountability associated with extended enterprise risk management. (Extended Enterprise Risk Management Survey, 2020,” Deloitte) |
63%Include IT leaders in the risk committee to help informed decision making. Currently 63% of chief technology officers are included in the C‑suite risk committee. (AICPA & NC State Poole College of Management) |
| Successful adoption of integrated risk management is often associated with these key elements. | |||
Assessment
Assess your organization’s method of addressing risk management to determine if integrated risk is possible
Assessing the organization’s risk maturity
Mature or not, integrated risk management should be a consideration for all organizationsThe first step to integrating risk management within the enterprise is to understand the organization’s readiness to adopt practices that will enable it to successfully integrate information. In 2021, we saw enterprise risk management assessments become one of the most common trends, particularly as a method by which the organization can consolidate the potential impacts of uncertainties or threats (Lawton, 2021). A major driver for this initiative was the recognition that information and technology not only have enterprise-wide impacts on the organization’s risk management but that IT has a critical role in supporting processes that enable effective access to data/information. A maturity assessment has several benefits for an organization: It ensures there is alignment throughout the organization on why integrated risk is the right approach to take, it recognizes the organization’s current risk maturity, and it supports the organization in defining where it would like to go. |

|
Integrated Risk Maturity Categories |

|
1 |
Context & Strategic Direction | Understand the organization’s main objectives and how risk can support or enhance those objectives. |
2 |
Risk Culture and Authority | Examine if risk-based decisions are being made by those with the right level of authority and if the organization’s risk appetite is embedded in the culture. | ||
3 |
Risk Management Process | Determine if the current process to identify, assess, respond to, monitor, and report on risks is benefitting the organization. | ||
4 |
Risk Program Optimization | Consider opportunities where risk-related data is being gathered, reported, and used to make informed decisions across the enterprise. |
Maturity should inform your approach to risk management
The outcome of the risk maturity assessment should inform how risk management is approached within the organization.

For organizations with a low maturity, remaining superficial with risk will offer more benefits and align to the enterprise’s risk tolerance and appetite. This might mean no integrated risk is taking place.
However, organizations that have higher risk maturity should begin to integrate risk information. These organizations can identify the nuances that would affect the severity and impact of risk events.
Integrated Risk Maturity Assessment
The purpose of the Integrated Risk Maturity Assessment is to assess the organization's current maturity and readiness for integrated risk management (IRM).
Frequently and continually assessing your organization’s maturity toward integrated risk ensures the right risk management program can be adopted by your organization.
| Integrated Risk Maturity Assessment
A simple tool to understand if your organization is ready to embrace integrated risk management by measuring maturity across four key categories: Context & Strategic Direction, Risk Culture & Authority, Risk Management Process, and Risk Program Optimization |
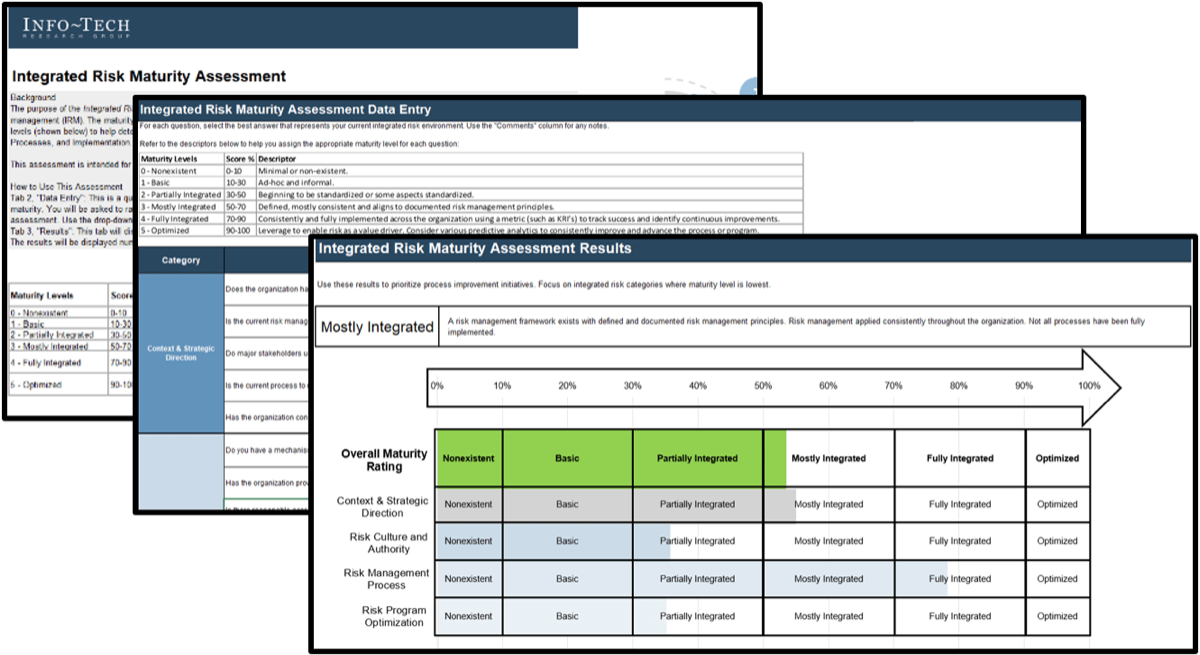
|
Use the results from this integrated risk maturity assessment to determine the type of risk management program that can and should be adopted by your organization.
Some organizations will need to remain siloed and focused on IT risk management only, while others will be able to integrate risk-related information to start enabling automatic controls that respond to this data.
Email Infographic
About Info-Tech
Info-Tech Research Group is the world’s fastest-growing information technology research and advisory company, proudly serving over 30,000 IT professionals.
We produce unbiased and highly relevant research to help CIOs and IT leaders make strategic, timely, and well-informed decisions. We partner closely with IT teams to provide everything they need, from actionable tools to analyst guidance, ensuring they deliver measurable results for their organizations.
MEMBER RATING
9.7/10
Overall Impact
$12,599
Average $ Saved
6
Average Days Saved
After each Info-Tech experience, we ask our members to quantify the real-time savings, monetary impact, and project improvements our research helped them achieve.
What Is a Blueprint?
A blueprint is designed to be a roadmap, containing a methodology and the tools and templates you need to solve your IT problems.
Each blueprint can be accompanied by a Guided Implementation that provides you access to our world-class analysts to help you get through the project.
Speed
×Talk to an Analyst
Our analyst calls are focused on helping our members use the research we produce, and our experts will guide you to successful project completion.
Book an Analyst Call on This Topic
You can start as early as tomorrow morning. Our analysts will explain the process during your first call.
Get Advice From a Subject Matter Expert
Each call will focus on explaining the material and helping you to plan your project, interpret and analyze the results of each project step, and set the direction for your next project step.
Unlock Sample ResearchAuthors
Valence Howden
Ibrahim Abdel-Kader
Brittany Lutes
Petar Hristov
Ian Mulholland
Contributors
- Daisha Penni, IT Risk Management, Oklahoma State University
- 6 additional anonymous contributors
Related Content: IT Governance, Risk & Compliance
Unlock Integrate IT Risk Into Enterprise Risk
Get Instant Access
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.
This content is exclusive to members.
Get instant access by signing up!
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.
Search Code: 98540
Last Revised: April 1, 2022
Book an Appointment
IT Research & Advisory Services
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.

 Optimize IT Governance for Dynamic Decision-Making
Optimize IT Governance for Dynamic Decision-Making
 Maximize Business Value From IT Through Benefits Realization
Maximize Business Value From IT Through Benefits Realization
 Build an IT Risk Management Program
Build an IT Risk Management Program
 Review and Improve Your IT Policy Library
Review and Improve Your IT Policy Library
 Establish a Sustainable ESG Reporting Program
Establish a Sustainable ESG Reporting Program
 Take Control of Compliance Improvement to Conquer Every Audit
Take Control of Compliance Improvement to Conquer Every Audit
 Establish an Effective System of Internal IT Controls to Mitigate Risks
Establish an Effective System of Internal IT Controls to Mitigate Risks
 Integrate IT Risk Into Enterprise Risk
Integrate IT Risk Into Enterprise Risk
 The ESG Imperative and Its Impact on Organizations
The ESG Imperative and Its Impact on Organizations
 Make Your IT Governance Adaptable
Make Your IT Governance Adaptable
 Build an IT Risk Taxonomy
Build an IT Risk Taxonomy
 Prepare for AI Regulation
Prepare for AI Regulation



