Transform Manufacturing by Mitigating the Challenges of Industry 4.0 and 5.0
Overcome stagnation by decoding the complexities of Industry 4.0 and 5.0.
Speak With A Representative
Request Content Access
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.
- The high cost of implementing advanced technologies, including initial investments in IT and OT, is a barrier for many manufacturers.
- Existing employees do not possess the necessary skills or know-how to work with these advanced technologies.
- The risk of cyberattacks increases in a connected and data-reliant manufacturing environment.
- It is difficult to properly manage the overwhelming volume of data generated by advanced manufacturing technologies.
- A cultural shift is required to establish effective human-machine collaboration.
- Manufacturers need to support significant changes in design, sourcing, operations, energy, and waste management to become more sustainable.
Our Advice
Critical Insight
CIOs can address the immediate challenges of Industry 4.0 and 5.0 adoption by fostering strategic partnerships with technology providers, engaging with research institutions, participating in industry consortiums, and conducting joint research and development initiatives with vendors to drive a culture of continuous learning and adaptation.
Impact and Result
Manufacturers have realized that successfully adopting Industry 4.0 and 5.0 technologies is essential to remain competitive. From incorporating principles of circularity to reducing costs and and controlling emissions, emerging technologies will have a transformative impact on the industry.
Info-Tech will provide:
Transform Manufacturing by Mitigating the Challenges of Industry 4.0 and 5.0 Research & Tools
1. Transform Manufacturing by Mitigating Challenges of Industry 4.0 and 5.0 Deck – A document that explores common Industry 4.0 and 5.0 adoption challenges and outlines the steps to mitigate them.
This research explores the unique roadblocks and challenges that prevent manufacturers from adopting Industry 4.0 and 5.0 technologies. This research contains a deep dive into these challenges and discusses associated mitigation strategies.
2. Industry Maturity Readiness Check Tool – A simple tool that assesses your readiness for adopting Industry 4.0 and 5.0 technologies.
This tool will help manufacturers assess their current industry maturity level along 37 unique dimensions across multiple functional areas.
Using this exercise, manufacturers can identify readiness levels across different functions at their organization, the gaps that exist between their current state and desired maturity level, and their overall performance against benchmarks from the manufacturing industry.
Speak With A Representative
Request Content Access
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.
Transform Manufacturing by Mitigating Challenges of Industry 4.0 and 5.0
Overcome stagnation by decoding complexities of Industry 4.0 and 5.0.
Analyst Perspective
Overcome stagnation by decoding complexities of Industry 4.0 and 5.0
The global manufacturing landscape is rapidly evolving. The integration of Industry 4.0 technologies has resulted in a more interconnected and data-driven manufacturing environment. Further, the leap to Industry 5.0 introduces additional layers of complexity, emphasizing customization, efficiency, and a more significant collaboration between humans and machines. This shift poses unique challenges, from technological adoption and workforce adaptation to ethical considerations and sustainability goals.
Key barriers exist and prevent a smooth transition. These include the high cost of implementation, lack of skilled talent, cybersecurity threats, vast amounts of data, and prevalent organizational culture. Ongoing economic uncertainty, rising interest rates, and fluctuations in labor costs and material prices make dealing with these challenges even more complex. Additionally, keeping up with the competition is becoming tougher; many manufacturers are experimenting with AI and other emerging technologies such as drones, autonomous guided vehicles, and robotics to accelerate value realization.
Adoption of Industry 4.0 and 5.0 requires manufacturers to take immediate action or risk being left behind. From the digitalization focus of Industry 4.0 to the sustainability and human-centric approach of Industry 5.0, CIOs are beginning to take the center stage in navigating these complexities effectively. By understanding the challenges and embracing the opportunities presented by Industry 4.0 and 5.0, manufacturers can not only optimize their operations but also drive innovation, competitiveness, and sustainable growth.

Shreyas Shukla
Principal Research Director, Manufacturing Industry
Info-Tech Research Group
Executive Summary
|
Your Challenge |
Common Obstacles |
Info-Tech’s Approach |
|---|---|---|
|
The high cost of implementing advanced technologies, including initial investments in IT and OT. Existing employees do not possess the necessary skills or know-how to work with modern, advanced technologies. The risk of cyberattacks increases in a connected and data-reliant manufacturing environment. Properly managing the overwhelming volume of data generated by advanced manufacturing technologies. Addressing the cultural shift required to establish effective human-machine collaboration. Supporting significant changes in design, sourcing, operations, energy, and waste management to become more sustainable. |
Capital required for investment in new technologies, infrastructure, and systems is a significant barrier. The shortage of qualified professionals to operate and maintain new systems and the extensive retraining or upskilling required to adapt to new technologies. The lack of robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive data and maintain operations. Integrating new technologies with existing systems and issues with compatibility between old and new equipment. Resistance to change from employees, management, or other stakeholders toward adoption of new technologies and processes. |
Manufacturers have realized that successfully adopting Industry 4.0 and 5.0 technologies is essential to remain competitive. From incorporating principles of circularity, reducing costs, and controlling emissions, emerging technologies will have a transformative impact on the industry. Info-Tech will provide: Actionable insights and recommendations to guide your journey through Industry 4.0 and 5.0 adoption. Case studies outlining how pioneering companies are navigating these challenges. An Industry Maturity Readiness Check tool for evaluating your readiness to adopt Industry 4.0 and 5.0 technologies. |
CIOs can address the immediate challenges of Industry 4.0 and 5.0 adoption by fostering strategic partnerships with technology providers, engaging with research institutions, participating in industry consortiums, and conducting joint research and development (R&D) initiatives with vendors to drive a culture of continuous learning and adaptation.
The majority of manufacturers are not meeting their goals
Manufacturers are reporting a significant drop in performance. This reflects the multitude of challenges that manufacturers are dealing with – geopolitical tensions, persistent labor shortage, high inflation, and increasing costs.

Manufacturers are also performing poorly on other key performance metrics.
In 2023,
- 74% did not achieve their inventory goals.
- 70% did not achieve their ROI goals.
- 69% did not achieve their sales goals.
- 69% did not achieve their cost savings goals.
“…analysis of Purchasing Managers’ Index (PMI) data reveals that the manufacturing sector was in contraction for most of 2023.”
– Deloitte Research Center for Energy & Industrials, 2023
Manufacturers are concerned about headwinds in the short term
Manufacturers continue to be under pressure from fragile supply chains, economic uncertainties, and talent shortages. Manufacturers are realizing that technology will play a key role in addressing these challenges. There is some optimism that digital transformation and smart factory initiatives will better position manufacturers to meet their business goals.
|
Supply chains continue to be impacted by geopolitical tensions and rising costs. |
Technology will enable manufacturers to address challenges and find effective ways of competing in the marketplace. |
|---|---|
|
84% of manufacturers are reevaluating or modifying their supply chain strategy in 2024. 51% of manufacturers believe that managing supply chain disruptions will be their top focus area in 2024. |
52% of manufacturers believe that a lack of new technology will be the top obstacle to meeting their 2024 business goals. 55% of manufacturers expect that they will have to spend more on tools, technology, and innovation in 2024. |
Sources: APQC, 2024; Deloitte Research Center for Energy & Industrials, 2023
“Disruptions drove $1.6 trillion in missed annual revenue growth.”
– Accenture, 2023
Manufacturers continue to focus on building operational resiliency
Manufacturers are focused on becoming resilient in this disruptive and volatile business environment. Manufacturers have realized that most global supply chains were never built to withstand the pressures they now face. Manufacturers are actively trying to balance the impact of black swan events, efficiency, responsiveness, and sustainability.
Top Short-term Priorities
|
Manage or reduce costs |
Automate processes and analytics |
Integrate & improve planning |
Reduce inventory levels |
Increase focus on sustainability & ESG |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
84% of manufacturers are focused on cost reduction. |
75% of manufacturers are focused on automation. |
67% of manufacturers are focused on improving planning. |
53% of manufacturers want to reduce inventory levels. |
52% of manufacturers want to increase focus on sustainability. |
Source: Alcott Global, 2023
Stable operations amid external volatility can only be achieved through resiliency.
Firms need to bolster their ability to react to disruptions and adapt accordingly, which is a short- to medium-term endeavor … long-term survival rests on a more profound transformation that understands how geopolitics, climate change, and technological advancement will shape the manufacturing industry and what manufacturers need to do to meet these sweeping changes.
Source: The Manufacturer, 2023
Manufacturers are actively allocating budgets toward smart technologies
Manufacturers are prioritizing investments in smart technologies. Powered by AI and data, these technologies enable manufacturers to make the necessary changes required to become more resilient, increase revenue, and reduce costs.
51%
“Compared to 2023, a larger proportion of organizations are planning to put in place new technologies and capabilities in 2024.”
– APQC, 2024

Source: Alcott Global, 2023
Smart technologies contribute to efficiency, productivity, and innovation
Application of smart technologies offers transformative benefits to manufacturers. Smart technologies facilitate greater supply chain transparency and agility, allowing manufacturers to respond more effectively to market demands and customer needs. The integration of these technologies builds a more connected, efficient, and adaptable manufacturing environment, leading to higher quality products and reduced operational costs.
|
Automation & Robotics Minimizes work-hours, improves productivity, quality |
Additive Manufacturing Enables rapid part production, allows innovation |
AGVs/AMRs Makes transport and mobility efficient in warehouses |
Remote Monitoring Enables visibility and reduces plant downtime |
|
Integrated SCM Optimizes production and reduces inventory cost |
Sustainability Reduces resource and energy cost and prevents wastage |
Advanced Planning Better forecasting, inventory mgmt., and work planning |
Cybersecurity Reduces risk of cyberattacks in a connected environment |
|
Asset Management Lowers TCO and improves maintenance |
Connectivity Enables real-time information sharing on shop floor |
Digital Twin Insights into performance and problems of equipment |
Data Analytics Increases product and process quality |
Manufacturers that have already adopted smart technologies are seeing clear benefits:
- 10% improvement in safety and sustainability
- 20% improvement in asset efficiency
- 30% improvement in product quality
- 30% reduction in operational costs
Source: Deloitte Research Center for Energy & Industrials, 2023
Regulation is driving advancements in industry maturity
Regulation is playing a significant role in adoption of Industry 4.0 and 5.0 technologies by manufacturers. European regulations have been focused on driving investments in green energy while American regulations are spurring investments in domestic manufacturing capability.
|
European Union |
United States of America |
|---|---|
|
In 2021, the European Union launched the NextGenerationEU plan, a EUR$800+ billion investment to repair the economic damage from COVID-19. This will have a significant impact on the manufacturing sector via:
|
The US introduced the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) and the CHIPS & Science Act in 2022. Both will have a significant impact on the domestic manufacturing sector by:
|
|
The NGEU plan resulted in:
Sources: Deloitte Insights, 2023; “EU Cohesion Policy,” European Commission, 2023; EMBER, 2023 |
The IRA resulted in:
Source: RMI, 2023 The CHIPS Act resulted in:
Source: Semiconductor Industry Association, 2022 |
Industry 4.0 and 5.0 emphasize different manufacturing philosophies
|
Industry 4.0 Smart Manufacturing |
Industry 5.0 Human-Centric Production |
|---|---|
|
Industry 4.0 enables digital transformation through technologies like IoT, AI, cloud computing, automating processes, and enhancing data-driven decision-making. This leads to significant gains in efficiency, productivity, and customization. The shift from traditional manufacturing to digital operations using advanced technologies. Automation of production processes, leading to improved efficiency and reduced human error. Optimization of processes, enhanced decision-making, and innovation using extensive data collection and analysis. Connected machines, devices, and systems that communicate with each other to streamline operations. The ability to produce customized products efficiently, adapting quickly to changing market demands. Protecting interconnected systems and sensitive data from cyberthreats. |
Industry 5.0 builds upon the digital foundation of Industry 4.0 to reintegrate human ingenuity, focusing on personalization, sustainability, and collaborative human-machine interaction. Human-centricity, human expertise, creativity, and adaptability. Sustainable and resilient operations are needed. Advanced technologies such as AI, cobots, augmented reality, digital twins, and additive manufacturing. Enabling better production planning, improved safety, and enhanced human-machine interaction. Productivity, skills development, workplace safety, work-life balance, and overall quality of life at work. The symbiosis between humans and cutting-edge technologies. |
Transition to higher industry maturity requires mitigation of unique challenges
Manufacturers must acknowledge and mitigate the unique challenges of trying to adopt Industry 4.0 and 5.0 technologies and philosophies. These challenges vary with the current state of your organization and associated mitigation strategies differ based on the desired level of maturity you are trying to achieve.

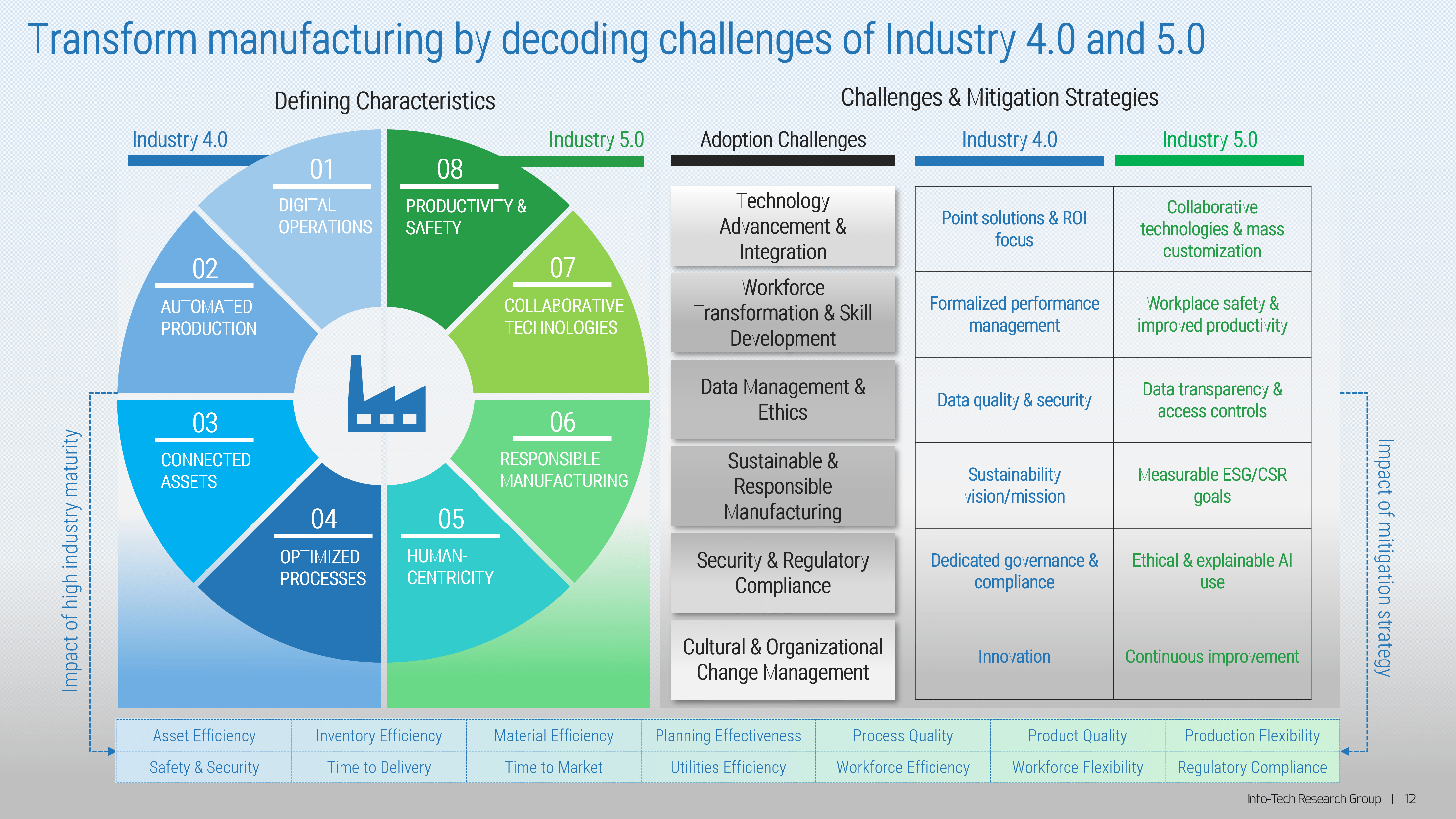
Adopting Industry 4.0 and 5.0 technologies has positive implications on productivity, quality, and flexibility
Industry 4.0 and 5.0 can have a profound impact on the way manufacturers operate. Together, they enable manufacturers to achieve a balance of technological innovation and human-centric values, paving the way for more resilient, adaptable, and sustainable manufacturing practices.
|
Productivity |
Quality |
Speed & Flexibility |
|---|---|---|
|
Company achieves the highest amount of output from the least amount of input. Asset & Equipment Efficiency Inventory Efficiency Utilities Efficiency Workforce Efficiency Material Efficiency |
Company is able to minimize defects in its products during manufacturing. Process Quality Product Quality Safety & Security |
Company is able to shorten product lifecycles, maximize sales and flexibility, & adapt quickly. Planning & Scheduling Effectiveness Production Flexibility Workforce Flexibility Time to Market Time to Delivery |
Industry 4.0 accelerates your needs while Industry 5.0 takes a societal view of transformation.
“The concept of Industry 5.0 is not based on technologies, but is centered around values, such as human-centricity, ecological or social benefits. … the technological transformation can be designed according to the societal needs, not vice versa.”
– “Enabling Technologies,” European Commission, 2020
Industry 4.0 implementation is falling short of expectations
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies to mitigate disruptions. While larger manufacturers have embraced a wide variety of Industry 4.0 technologies, small and medium businesses are continuing to show hesitation. Digitization and technology modernization continues to remain a priority across the board; however, many manufacturers are slowing down Industry 4.0 adoption and instead choosing to deal with other business priorities.
|
While … |
The reality is … |
|---|---|
|
86% of manufacturers believe that smart technologies will make them more competitive. 67% of manufacturers agree that adopting Industry 4.0 technologies would be beneficial. |
39% of manufacturers do not have adequate budgets to invest in Industry 4.0 technologies. 33% of manufacturers have a formal Industry 4.0 roadmap under development. 32% of manufacturers feel that Industry 4.0 initiatives have decelerated. 53% of manufacturers continue to deal with lack of skilled employees. 57% of manufacturers say that they are only partially secure against cyberattacks. 19% of manufacturers have a fully formed cybersecurity program. 43% of manufacturers are using AI/ML in some form in their organization. 25% of manufacturers are using digital twin technology in some form. 20% of manufacturers feel they have adequate network capabilities to support advanced technologies. |
Sources: MLC Research, 2022, as qtd. in NAM, 2022; Deloitte Research Center for Energy & Industrials, 2023
Manufacturers must solve diverse and evolving challenges to transition to higher industry maturity
Manufacturers will need to acknowledge and resolve unique challenges while trying to adopt Industry 4.0 and eventually 5.0 level maturity. The transition from lower maturity levels to Industry 4.0 and 5.0 sees challenges evolve from dealing with basic automation and data handling to integrating complex, smart technologies and, finally, balancing advanced technology with human-centric and sustainable approaches.
Industry 4.0
- Integration
- Data Management
- Cybersecurity
- Reskilling
- Culture
- Supply Chain
- Quality Management
- Compliance
- Investment & ROI
- Reliability
Industry 5.0
- Automation
- Sustainability
- Ethical AI
- Mass Customization
- Human-Robot Collaboration
- Social Responsibility
- Continuous Improvement
- Data Privacy & Ethics
- Problem Solving
- Agility
Source: Contributor Interviews, 2024
Summary of common challenges in achieving Industry 4.0 maturity level
Challenges to Industry 4.0 adoption
|
Challenges |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Integration |
Incorporating IoT, AI, and cloud computing into existing manufacturing setups. |
|
Data Management |
Establishing systems for collecting, storing, and analyzing large volumes of data. |
|
Cybersecurity |
Protecting increasingly digital and interconnected systems from cyberthreats. |
|
Reskilling |
Training existing employees in new digital skills and attracting talent proficient in emerging technologies. |
|
Culture |
Moving organizational culture from traditional manufacturing mindsets to embracing digital transformation. |
|
Supply Chain |
Adapting supply chains to be more flexible and integrated with smart technologies. |
|
Quality Management |
Implementing predictive maintenance and ensuring quality in a more automated environment. |
|
Compliance |
Adapting to new regulations and standards that come with digital transformation. |
|
Investment & ROI |
Balancing the high costs of smart technology investments with expected returns. |
|
Reliability |
Ensuring the reliability of new technologies and the stability of production processes during transition. |
This list is representative and not exhaustive.
Source: Contributor Interviews, 2024
Summary of common challenges in achieving Industry 5.0 maturity level
Challenges to Industry 5.0 adoption
Challenges | Description |
|---|---|
Automation | Integrating advanced automation (AI, robotics) while enhancing human skills and creativity. |
Sustainability | Embedding sustainable and eco-friendly practices into production processes. |
Ethical AI | Addressing ethical concerns related to AI decision-making and its impact on employment. |
Mass Customization | Achieving mass customization and personalization in production without compromising efficiency. |
Human-Robot Collaboration | Safely and effectively integrating collaborative robots (cobots) into the workforce. |
Social Responsibility | Aligning manufacturing practices with broader social goals and community wellbeing. |
Continuous Improvement | Keeping pace with rapid technological advancements and continuously innovating. |
Data Privacy & Ethics | Managing the increased personal data usage with respect for privacy and ethical considerations. |
Problem Solving | Developing solutions for complex challenges that arise from advanced human-machine interactions. |
Agility | Maintaining flexibility in manufacturing processes to quickly adapt to market or environmental changes. |
This list is representative and not exhaustive.
Source: Contributor Interviews, 2024
Analysis of challenges reveals common themes that manufacturers need to address
Technology advancement, integration, workforce transformation, and skill development are the most pressing challenges that manufacturers need to address in their transition to a higher level of industry maturity. Additionally, manufacturers will need to transform data management, cybersecurity, compliance, and organizational culture and manage their sustainability objectives in this journey to get to Industry 4.0 and beyond.

“Industries are spending over US$1 trillion a year in digital factory transformation, with the automotive & transportation industry accounting for nearly 10% of the share.”
– Statista, 2023
Six core roadblocks prevent manufacturers from adopting Industry 4.0 and 5.0 technologies
|
Common roadblocks for Industry 4.0 & 5.0 adoption |
Technology advancement & integration |
Roadblocks that arise from dealing with current state technology and decisions related to technology upgrades. |
|---|---|---|
|
Workforce transformation & skill development |
Roadblocks that arise from the workforce lacking the skills, knowledge, and know-how to use and maintain advanced technologies. |
|
|
Data management & ethics |
Roadblocks arising from the absence of critical data, use of incorrect or aged data, or lack of use of data for analysis or decision-making. |
|
|
Sustainable & responsible manufacturing |
Roadblocks arising from inefficient manufacturing practices including inefficient use of resources and energy. |
|
|
Security & regulatory compliance |
Roadblocks arising from the heightened cyberthreats to connected assets and use of noncompliant equipment or practices. |
|
|
Cultural & organizational change management |
Roadblocks arising from the unwillingness and inability of employees to support and change in the face of maturity transition initiatives. |
Info-Tech’s approach and team can help, irrespective of where you are in your digital journey
|
Starting → Benefitting |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Where are you on the journey? |
Establish your digital North Star |
Quantify the value of digital use cases |
Create the digital roadmap |
Deliver digital use cases and realize impact |
Create the infrastructure to drive and sustain change |
|
Set aspiration: Vision setting with key business unit (BU) stakeholders to discuss and align on digital aspiration (e.g. Big-T vs. Mini-T, self-funded, and slow burn vs. investments) |
Assess opportunity: Comprehensive end-to-end (E2E) understanding of the digital opportunity across BU/functions (e.g. data analysis, process walks, interviews) |
Design and plan: Bottom-up initiative design and planning (e.g. opportunity to initiatives, financials, phasing, design principles) |
Execute: Detailed initiative builds and implementation; execution with rigor and transparency (e.g. process optimization then automate, test, measure, scale) |
Enable: Transformation infrastructure, operating model, and culture to drive value capture and sustain change |
|
|
Examples of how Info-Tech can help |
Digital North Star placemat (e.g. industry trends, top-down opportunity, high-level planning) |
Digital maturity assessments (e.g. current state digital adoption and transformation readiness) Opportunity assessments |
Initiative bottom-up design Holistic initiative planning |
Initiative build Initiative implementation Value assurance assessment |
Transformation infrastructure IT modernization Change management Performance management Workforce management |
The following content will provide an overview of the common challenges that prevent manufacturers from adopting higher maturity technologies. This will support your organization in locating the Digital North Star, assessing your current state of digital maturity and readiness to adopt Industry 4.0 and 5.0 technologies.
*Note: This does not provide the challenges specific to your organization. To do that, you will have to complete the exercise outlined toward the end of this document.
Email Infographic
About Info-Tech
Info-Tech Research Group is the world’s fastest-growing information technology research and advisory company, proudly serving over 30,000 IT professionals.
We produce unbiased and highly relevant research to help CIOs and IT leaders make strategic, timely, and well-informed decisions. We partner closely with IT teams to provide everything they need, from actionable tools to analyst guidance, ensuring they deliver measurable results for their organizations.
What Is a Blueprint?
A blueprint is designed to be a roadmap, containing a methodology and the tools and templates you need to solve your IT problems.
Each blueprint can be accompanied by a Guided Implementation that provides you access to our world-class analysts to help you get through the project.
Talk to an Analyst
Our analyst calls are focused on helping our members use the research we produce, and our experts will guide you to successful project completion.
Book an Analyst Call on This Topic
You can start as early as tomorrow morning. Our analysts will explain the process during your first call.
Get Advice From a Subject Matter Expert
Each call will focus on explaining the material and helping you to plan your project, interpret and analyze the results of each project step, and set the direction for your next project step.
Unlock Sample ResearchAuthor
Shreyas Shukla
Contributors
- Ranga Bodla, VP, Field Engagement & Marketing, NetSuite
- Chad Sindhu, Senior Partnerships Specialist, Gramener
- Adil Bukhari, Research Analyst, Insights Driven Research
- Ashraf Qureshi, Digital Executive, Global Market Estimates
- Vivek Kalyan Ramakrishnan, Consulting Director, Global Technology Consulting Firm
- Fredy M., IT Architecture & Development Manager, Regional Industrial Manufacturing Company
- Dr. Diganggana Talukdar, Research Associate, Knowledge Ridge
Unlock Transform Manufacturing by Mitigating the Challenges of Industry 4.0 and 5.0
Get Instant Access
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.
This content is exclusive to members.
Get instant access by signing up!
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.
Search Code: 104618
Last Revised: May 8, 2024
TAGS:
advanced analytics, agile methodology, artificial intelligence, automation, change management, challenges, collaboration, continuous improvement, cybersecurity, data analytics, data protection, digital first mindset, digital transformation, employee training, ethical AI, flexibility, green manufacturing, human-robot interaction, Industry 4.0, Industry 5.0, innovation, intellectual property, IoT, machine learning, manufacturing processes, market adaptability, predictive maintenance, quality control, real-time data, resilience, risk management, roadblocks, ROI analysis, social impact, sustainability, supply chain management, technology integration, workforce skillsBook an Appointment
IT Research & Advisory Services
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.




