Unlock Ensure Business Alignment in Managed Service Agreements
Get Instant Access
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.
Ensure Business Alignment in Managed Service Agreements
Prepare your organization to maximize value from your managed service providers.
More and more organizations are turning to managed service providers (MSPs) to streamline IT operations, enhance efficiency, and gain access to specialized expertise. However, as reliance on MSPs increases, so does the importance of ensuring their contracts are built to maximize the value of the relationship. This blueprint provides a comprehensive, step-by-step approach to drafting an effective, business-aligned managed service contract.
With the MSP market expected to triple in the next ten years, learning how to draft a managed service contract that meets operational and organizational needs will be critical. These agreements define the foundation of a partnership that will directly impact your organization’s strategic outcomes… for better or for worse.
Do it right to get it right.
Building a comprehensive, business-aligned managed service contract is not about reinventing the wheel but pursuing the right process, rigorously. The foundation lies in basic yet critical steps – follow the right ones to set the stage for long-term value.
Build out contract management capabilities.
For small and medium-sized organizations, many of which lack a formal vendor management practice, building a foundational understanding of contract management is essential to mitigate risks and maximize value. Even in large enterprises, broader vendor management capabilities will ensure contracts are aligned with business goals and operational needs to drive long-term success.
Lay the groundwork for success, leaving no stone unturned.
What you put in your contract is up to you, not the MSP. Creating an effective managed service contract starts with clearly identifying the outcomes you expect, the terms required to achieve those outcomes, and how to negotiate and enforce those terms – all before you even share the first draft with the service provider.
Use our comprehensive methodology to ensure your managed service agreements deliver their expected value and performance.
Our research guides you through a comprehensive approach to building a managed service contract that prioritizes measurable outcomes, aligns with organizational goals, and adapts to an evolving IT landscape. We provide step-by-step guidance in a comprehensive three-phased approach that turns your managed services into strategic assets. Use this blueprint to:
- Review and align your business objectives, engagement model, and service scope with the wider organization’s expectations and goals.
- Establish measurable metrics to clearly delineate requirements and ensure the expected value will be delivered.
- Review and integrate all critical risk management aspects, regulatory compliance requirements, and any other legal aspects that have been covered in the contract.
Ensure Business Alignment in Managed Service Agreements Research & Tools
1. Ensure Business Alignment in Managed Service Agreements Storyboard – A step-by-step blueprint to prepare your organization to maximize value from your managed service providers.
This storyboard outlines a three-phased process to review a draft of a managed service contract:
- Review your business objectives and align the engagement model and service scope with the organization’s expectations.
- Revisit the SLAs, KPIs, and governance of value and performance in alignment with the organization’s expectations.
- Validate risk and compliance management including disaster recovery, business continuity, and exit options.
2. Managed Service Contract Review Workbook – An Excel-based workbook containing a set of tools and templates used in this blueprint’s activities.
The tools and templates included in this workbook guide you through the development of an organization-aligned service agreement, including:
- Model Validation
- Vendor Selection Rubric
- Service Scoping
- Roles & Mandates
- OCI Responsibility Matrix
- Staffing Plan
- Risk Register & Risk Matrix
3. Sample Managed Service Agreement – A Word-based template to assist you in drafting a managed service contract.
This template provides examples of key sections in a managed service agreement, such as Overall Scope of Work and Solution Proposal.
4. Managed Service Agreement Evaluation Tool – An Excel-based tool to assess a proposed contract from an MSP to ensure business alignment.
This tool guides you through a robust review and evaluation process for draft managed service agreements before they are signed. Use this tool to identify and prioritize the terms, conditions, and clauses that are critical to your organization. If you are drafting the contract from scratch, use this tool as a checklist to ensure it is fully aligned with your organization’s expectations.
5. Managed Service Agreement Taxonomy – A Managed Service Procurement Model and IT Vendor Management Taxonomy to familiarize users with the key terms and phrases used in this blueprint.
This taxonomy includes terms, definitions, examples, and case studies related to the managed service procurement model and IT vendor management disciplines. Use this file to understand key terms and phrases.
Member Testimonials
After each Info-Tech experience, we ask our members to quantify the real-time savings, monetary impact, and project improvements our research helped them achieve. See our top member experiences for this blueprint and what our clients have to say.
10.0/10
Overall Impact
$81,225
Average $ Saved
110
Average Days Saved
Client
Experience
Impact
$ Saved
Days Saved
Testimonial
CELL THERAPY CATAPULT LIMITED
Guided Implementation
10/10
$81,225
110
Best parts - open honest and challenging conversations in supportive environment - Thanks
Ensure Business Alignment in Managed Service Agreements
Prepare your organization to maximize value from your managed service providers.
Analyst perspective
Building a comprehensive, business-aligned managed service contract is not about reinventing the wheel but pursuing the right process rigorously.

Manish Jain
Principal Research Director, CIO Strategy
Info-Tech Research Group
When Emily Bennett, CIO of Acme Corporation, faced the task of outsourcing an IT service through a managed service contract, she recalled a painful lesson from her past. A previous contract, though flawless on paper, had failed to deliver value because it didn’t align with business goals.
Determined not to repeat the mistake, Emily approached the new agreement with a fresh perspective. She gathered her leadership team and their vendor, Zenith IT Solutions, for a five-day workshop with an outside contract management expert. Together, with a well-defined process, they reviewed and reframed the contract – not just as a list of services but as a strategic partnership.
Instead of focusing solely on technical service level agreements (SLAs), they defined metrics tied directly to business outcomes, like time to market and customer satisfaction. They outlined shared responsibilities, a governance model for accountability, and flexible terms to adapt to future needs.
Six months later, Acme’s outsourced platform was thriving, supported by a contract that didn’t just manage services but aligned with the company’s strategic objectives. Emily smiled, knowing this wasn’t just a contract – it was a foundation for trust and long-term success.
Although this is not a real story, the smile on Emily’s face can be real for you, the CIO, and your team.
This blueprint will walk you through the process of reviewing the draft of your managed service contract and ensuring that it defines a clear scope and role for the service provider and your team and embeds a governance structure that actively monitors service value and performance.
This methodology emphasizes a strategic approach – one that prioritizes measurable outcomes, aligns with organizational expectations, and adapts to an evolving IT landscape.
Is this the right research blueprint for you?
This Research Is Designed For:
-
The CIOs and IT leaders who:
- Have already released RFPs for IT service and received proposals from their managed services providers (MSPs).
- Want to maximize value by aligning their managed service agreement with their organizational expectations.
-
Directors or managers who:
- Are part of IT procurement or the vendor management office (VMO) and are responsible for managing IT service providers.
- Are responsible for writing the contract, negotiating with MSPs, and/or administering the contract.
This Research Will Help Them:
-
Ensure business alignment in your managed service agreements by using the Managed Service Agreement Evaluation Tool and other tools alongside this storyboard to:
- Provide options related to various clauses in the managed service agreement.
- Clarify strategic objectives, define scope precisely, and validate vendor responsibilities.
- Review commercial aspects of the contract and key terms and conditions (T&Cs).
- Integrating performance and risk management in the contract.
- Validating that exit and termination options align with your organizational realities and environment.
This Research Will Also Assist:
- IT service managers
- IT procurement teams
- Contract management teams
- Senior IT leadership
This Research Will Help Them:
- Understand various T&Cs written in managed service agreements.
- Understand the importance of agreed-upon contracts and conditions to extract more value from service providers.
- Understand internal and external obligations emerging from the managed service agreement.
Refer to Managed Service Contract Taxonomy for full taxonomy.
Executive summary
Your ChallengeAs a tech CxO, outsourcing some or most of your IT services is an integral aspect of your IT operating model. However, your organization usually engages with providers in a way that may not benefit it – or may even harm it. Your challenge includes aligning strategic needs, managing stakeholder expectations, ensuring contract flexibility, and managing risks while balancing relationships – all while supporting future growth and minimizing dependency. However, most of the time, you either become subservient to the provider or very prescriptive by focusing on how something should be done instead of what should be done. Either scenario results in contracts that are verbose but not business-aligned, executable, or enforceable. |
Common ObstaclesYour organization is not as mature as large enterprises in its outsourcing practices. Somebody in the hierarchy may have already decided that a particular provider should be awarded a contract and that you should use a specific model. You may not even have a dedicated vendor management function or VMO, prohibiting your team from creating the right contracts when it wants to outsource IT work to one or more MSPs. Moreover, outcomes your organization expects from the contracts are not well articulated, resulting in unnecessary complexities in defining business-aligned SLAs. On top of that, lacking a forum to engage with vendors regularly makes managing contract performance difficult. |
Info-Tech’s ApproachAs your organization is likely outsourcing some or most of its IT services, building business-aligned contracts is the way to reduce strategic and operational risks. Info-Tech proposes a three-phased approach to ensure your managed service contracts are business-aligned and deliver expected value and performance:
Leverage the Managed Service Agreement Evaluation Tool to ensure business alignment in managed service agreements. |
Info-Tech Insight
The key to creating a comprehensive managed service contract is thinking about what outcomes you are expecting, what terms are required to achieve those outcomes, and how you would negotiate and enforce each term, even before you share the first draft with the service provider.
What is managed service (and what isn’t it)?
Predictable Pricing
Price not necessarily fixed but highly predictable for a specific scope.
Provider Responsible for Operational Management
Client not responsible for day-to-day management of resources.
Scalability and Flexibility
Very specific scope but equipped with a defined change management process.
Better Capability or Not a Core Competency
Provider is more capable than the client to deliver on the service in scope, or the service is not client’s core competency.
Defined Service-Level Agreement
Define only what is expected, not how it should be done
Any service being delivered and expected to follow these five characteristics is a managed service. However, failing any of these characteristics means it is not a managed service.
Refer to Managed Service Agreement Taxonomy for full taxonomy.
The MSP market is growing, but not all providers are the same
Just because you are procuring an IT service from an MSP doesn’t mean you are procuring a managed service.

 75% of their revenue from managed services and Hybrid MSPs provide managed services alongside other offerings." loading="lazy">
75% of their revenue from managed services and Hybrid MSPs provide managed services alongside other offerings." loading="lazy">
Info-Tech Insight
While IT services are expected to have a CAGR of 2% to 4% over the next 10 years, the IT managed service market is expected to grow 3x to about $400 billion by the end of 2024 and to about $1.2 trillion in the next 10 years. Much of the estimated growth in IT services is expected to come from adoption of the managed service model for IT services by the hybrid MSPs, and that’s why drafting business-aligned managed service agreements is extremely critical.
Managed service IT models are growing in popularity, but value expectations are not the same
Ensure that you have articulated your organization’s expectations before engaging in managed service.

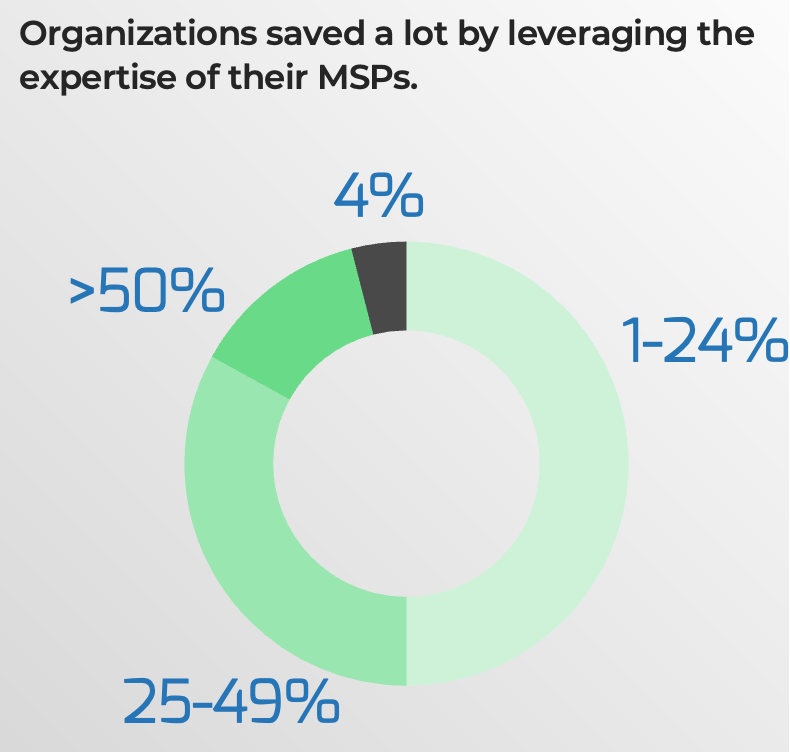
According to CompTIA, of all organizations that engaged with an MSP:
- 4% reported to save nothing
- 50% saved 1% to 24% in annual IT costs
- 33% saved 25% to 49%
- 13% saved more than 50%
Source: CompTIA 2022
Understand the key challenges of engaging in managed services
When engaging in a managed service, you are working with an organization that is likely different from your organization in its culture, policies, and practices.
Balancing Strategic and Operational Needs
Trying to balance long-term strategic objectives (e.g. innovation) and operational requirements (e.g. immediate cost saving) can lead to conflicting priorities.
Managing Stakeholder Expectations
Aligning diverse expectations from different departments and executives, each with unique goals, can complicate contract requirements and agreement.
Ensuring Flexibility for Future Change
Designing a contract that supports evolving technologies and business needs without locking the organization into rigid terms is a complex task.
Managing Risk
Clearly defining responsibility for potential risks and service failures requires careful negotiation to prevent future misunderstandings.
Managing Value and Relationships
Building a collaborative relationship while maximizing value and avoiding overreliance on a single vendor can be tricky, especially with critical service dependencies.
Be aware of common obstacles when engaging in managed services
These barriers make engaging in managed services even more challenging:
At the time of drafting agreements:
- Vague scope of services
- Ambiguity in performance metrics and SLAs
- Poorly defined governance structure
- Unclear responsibilities and roles
- Insufficient risk management and compliance
- Lack of adaptability to future needs or technology changes
At the time of executing agreements:
- Misalignment between contract terms and operational realities
- Poorly defined communication hierarchy
- Ambiguous dispute resolution system
- Unclear criteria for change requests
- Lack of continuous performance monitoring
- Ambiguous RACI
Inefficient contracts and contract management practices cost millions.
Poor contract management continues to cost companies 9% of their bottom line.
Source: World Commerce and Contracting (April 2020)
As of 2024, the GDPR has levied noncompliance penalties nearing 5 billion euros. Many of these fines had their geneses in ambiguous agreements between multiple parties.
Source: Data Privacy Manager, 2024
Map out your key managed services risks…

Refer to Tab 6b, Risk Matrix, in the Managed Service Contract Review Workbook.
…And understand these risks in more detail
Ambiguous Scope of Work
Failing to clearly define the scope of services leads to misunderstandings and disputes.
Inappropriate Commercial Model
Being unable to assess the pros and cons of contracting models leads to unexpected bills and misalignment with organizational expectations.
Unclear SLAs
Vague or unrealistic SLAs lead to stakeholder dissatisfaction and conflicts. SLAs must be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
Inadequate Performance Metrics
Assessing the success of services without proper metrics is challenging. Contracts should include clear performance metrics and methods for measuring them.
Lack of Flexibility
Lack of flexibility may result in outdated or ineffective services. Contracts should account for changes in technology, business needs, and regulations. For Example, include built-in flexibility to scale service levels (additional resources and resource reduction) as demand fluctuates and pricing transparency when flexibility measures are exercised.
Poorly Ambiguous Responsibilities & Language
Ambiguity leads to finger-pointing and delays in issue resolution. All parties should have clearly defined roles and responsibilities including having communication/relationship mapping between provider and client stakeholders (steering as well as transactional), from the C-suite down to line-level staff.
Insufficient DRP and BCP
As disruptions are part of business, failure to plan for these scenarios can lead to significant delays. Contracts should address how the service provider will handle disasters and ensure business continuity.
Limited or Unclear Communication Protocols
Poor communication leads to misunderstandings and delays in addressing problems. Communication plans should clearly articulate role mapping, frequency and agenda of meetings, and reports such as BAM/QBR meetings, status reports, etc.
Inadequate Security Measures
Failure to address security concerns can result in breaches and data loss, major challenge for the organization. Security measures should be clearly outlined to protect sensitive data and systems.
Failure to Address Change Management
Contracts should include a process for managing changes to services, including how changes will be requested, evaluated, and implemented.
Neglecting Relationship Management
Neglecting this aspect leads to poor collaboration and contract dissatisfaction. Building a strong relationship between the service provider and the organizational leadership is essential.
Inadequate Data Processing Agreement
Not having adequate data processing measures in place may lead to major monetary penalties, especially if you are in a jurisdiction governed by the GDPR or similar regulations. So, ascertain data processing role and responsibility.
Refer to Tab 6b, Risk Matrix, in the Managed Service Contract Review Workbook.
A business-aligned contractual agreement is key to success in managed service engagement
Driving success through strategic alignment – a business-aligned contract transforms services into strategic assets.

Key elements for business alignment in managed service agreements:
- Clear Business Objectives: Outline precise goals the contract should support.
- Defined Scope and Requirements: Set clear parameters for services.
- Service Levels & KPIs: Ensure SLAs and KPIs are tied to business outcomes.
- Risk & Flexibility Provisions: Address adaptability for changing needs.
- Governance & Review Mechanisms: Establish oversight for continuous alignment.
And building trust into the vendor relationship drives flexibility within and beyond the contract
“It's a two-way street. As a client, we always asked, ‘What can we do better as a customer to make you, as a vendor, more successful?’ It needs to be a win-win.”
– Sarah Pletcher
“The relationship matters; when contracts are treated as separate from the relationship, they risk becoming outdated or ineffective in the face of changing business needs.”
– Kate Vitasek
Build trust through…
- Transparent Communication: Emphasize regular, open updates.
- Shared Goals: Align on long-term objectives.
- Mutual Respect: Value each party’s expertise and input.
- Genuine, Honest Feedback: Provide and receive honest performance insights.
Flexibility results in…
- Adaptability to Change: Much easier adjustments to contract terms, if needed.
- Innovation Potential: Encourages joint exploration of new solutions.
- Reduced Risk: Trust leads to smoother issue resolution.
- Relationship Maturity: Paves the way for shared outcomes and risks
Case study – brief
Contractual flexibility is the litmus test of the longevity of a managed service contract.
Industry
Payments
Source
Info-Tech Research Group
Situation
In a significant project for a payment solutions organization*, an IT executive was tasked with replacing an existing contact center solution, a decision involving a hefty commitment of $2 million to $3 million over three years.
This initiative was crucial, as the contact center was essential for supporting external clients.
The executive recognized the need for an approach that would ensure that the new solution would meet current requirements and align with the organization’s future goals.
Approach
The executive embarked on the project with a detailed RFP process that allowed her to articulate the organization’s current and future needs.
She leveraged various aspects of contract management and negotiation to achieve success. Key aspects around which she structured the whole service provider engagement were:
- Detailed RFP development
- Service provider engagement
- Contract negotiation
- Identifying gaps and mitigating risks
- Continuous connect with business
- Contractual flexibility
Result
The transition to the new contact center solution was successfully executed, with the organization achieving substantial cost savings and aligning the new service with both current and future operational needs.
The executive's proactive contract management approach not only facilitated a smoother service provider relationship but also equipped her team to avoid common pitfalls associated with contract negotiations.
This experience underscored the importance of thorough preparation, clear communication, and flexibility in contract management, ultimately leading to a successful implementation that enhanced the overall client support experience.
*Anonymous large Canadian payment solution company
Case approach – contractual flexibility gives the negotiation power
Flexibility in contract terms leads to long-term contract sustainability. Review contract terms, especially for long-term (more than a year) contracts, to highlight instances that are extremely specific to current business scenarios and may not be flexible enough to accommodate small variations due to changes in the business environment.
Detailed RFP
The RFP was meticulously crafted to include all business requirements and future objectives. This proactive approach helped the executive gather comprehensive service provider responses that addressed both immediate and strategic needs.
Identifying Gaps and Mitigating Risks
Throughout the implementation phase, the executive remained engaged with the service provider to clarify and address potential issues. Despite the thorough RFP process, unforeseen "gotchas" surfaced, particularly regarding the migration of call recordings. The organization initially overlooked the necessity of this requirement, leading to additional costs.
Service Provider Engagement
The selection process involved extensive service provider reviews, including months of discussions and product demonstrations. This allowed for a thorough understanding of each service provider’s capabilities, as well as their roadmaps, ensuring that they aligned with the organization's long-term vision.
Continuous Connection With Business
By recognizing the business's priorities, the executive effectively navigated the situation. After consulting with the legal team, it was determined that the migration of older call recordings was unnecessary for legal purposes. This insight helped the business avoid unnecessary expenditures and focus on more relevant training resources.
Contract Negotiation
With a negotiation period lasting two and a half months, the executive showcased her negotiation skills, ultimately saving the organization nearly $1 million on the contract. During negotiations, she emphasized critical contract aspects such as data residency, data privacy, and PCI compliance. This focus was vital, especially since the new solution was cloud-based.
Contractual Flexibility
She ensured that the contract included language that allowed for negotiation and problem-solving with the service provider. This foresight was crucial in addressing unexpected challenges, enabling a collaborative approach to resolving issues.
Info-Tech’s methodology for assuring business alignment in managed service agreements
Phases |
1. Contract Scope Alignment |
2. Value and Performance |
3. Risk and Compliance |
Phase Steps |
|
|
|
Phase Outcomes |
|
|
|
Ensure Business Alignment in Managed Service Agreements
Building a comprehensive contract is not about reinventing the wheel but about pursuing the right process rigorously.

Blueprint deliverables
Each step of this blueprint is accompanied by supporting deliverables to help you accomplish your goals:
Managed Service Contract Review Workbook
This Excel workbook contains a set of tools and templates – including model validation, a vendor selection rubric, service scoping, a traceability matrix, roles and mandates, an OCI responsibility matrix, a staffing plan, and a risk register & risk matrix – that will help you bridge any gaps found during the contract review process.
Sample Managed Service Agreement
This Word template contains key sections like Overall Scope of Work and Solution Proposal that you may be able to use to draft a managed service contract.
Managed Service Agreement Taxonomy
This taxonomy file comprises terms, definitions, examples, and case studies related to the managed service procurement model and IT vendor management disciplines. Many of them are directly referred to in this blueprint, and others are required to understand the context.
Key deliverable:
Managed Service Agreement Evaluation Tool
Use this tool to review the draft of a managed service agreement before it is signed and to identify and prioritize the terms, conditions, and SLAs that are critical to your organization.
If you are drafting a contract from scratch and not provided one by the service provider, you may use this tool along with the Sample Managed Service Agreement as a checklist to ensure it is fully aligned with your business expectations.
Your organization should aim for a "fair deal" set of clauses that will provide the required protection for the buyer and remain fair to the vendor.
Blueprint benefits
IT Benefits
- Effort and Cost Saved: Provides a structured approach that reduces ambiguity and ensures all critical elements are addressed, saving effort and cost in creating a comprehensive managed service contract.
- Better Risk Management: Preempt potential risks early and respond with relevant clauses in the contract for better risk management and contract stability.
- Improved Vendor Relationships: Align the organization’s IT team and vendor stakeholders for more effective service delivery and collaboration.
Business Benefits
- Cost Efficiency: Improve cost control and visibility by defining clear terms and avoiding unnecessary and unforeseen expenses.
- Reduced Legal and Compliance Risks: Minimize legal disputes and increase adherence to regulatory requirements to preserve management bandwidth and protect the business.
- Enhanced Agility: Strengthen the vendor relationship for more flexibility in contract execution, enabling the organization to adapt to evolving technology and business needs quickly.
Measure the value of this blueprint
Measure |
Description |
| Cost Savings | Track reduction in unplanned/unexpected costs, disputes, or penalties due to clearer contract terms. |
| Service Uptime/Performance | Measure improvements in vendor performance and adherence to SLAs. |
| Contracting Cycle Time | Assess the reduction in the contracting cycle time (i.e. time to draft, negotiate, and finalize contracts). |
| Stakeholder Satisfaction Index | Gather feedback on improved clarity and effectiveness of contracts. |
| Vendor Relationships Score | Evaluate the quality of collaboration and trust with service providers. |
| Overall Risk Profile Score | Assess the perception of reduced risk and compliance issues across departments. |

Figure: an illustration containing sample data
Email Infographic
About Info-Tech
Info-Tech Research Group is the world’s fastest-growing information technology research and advisory company, proudly serving over 30,000 IT professionals.
We produce unbiased and highly relevant research to help CIOs and IT leaders make strategic, timely, and well-informed decisions. We partner closely with IT teams to provide everything they need, from actionable tools to analyst guidance, ensuring they deliver measurable results for their organizations.
MEMBER RATING
10.0/10
Overall Impact
$81,225
Average $ Saved
110
Average Days Saved
After each Info-Tech experience, we ask our members to quantify the real-time savings, monetary impact, and project improvements our research helped them achieve.
What Is a Blueprint?
A blueprint is designed to be a roadmap, containing a methodology and the tools and templates you need to solve your IT problems.
Each blueprint can be accompanied by a Guided Implementation that provides you access to our world-class analysts to help you get through the project.
You Get:
- Ensure Business Alignment in Managed Service Agreements Storyboard
- Managed Service Contract Review Workbook
- Sample Managed Service Agreement
- Managed Service Agreement Evaluation Tool
- Managed Service Agreement Taxonomy
Need Extra Help?
Speak With An Analyst
Get the help you need in this 3-phase advisory process. You'll receive 9 touchpoints with our researchers, all included in your membership.
Guided Implementation 1: Contract Scope Alignment
- Call 1: Business alignment and objectives check
- Call 2: Scope and requirements
- Call 3: Vendor solution and responsibility validation
Guided Implementation 2: Value and Performance
- Call 1: SLA and KPI evaluation
- Call 2: Governance and performance management
- Call 3: Commercial terms and flexibility
Guided Implementation 3: Risk and Compliance
- Call 1: Risk management and business continuity
- Call 2: Compliance and regulatory alignment
- Call 3: Termination and exit options
Author
Manish Jain
Contributors
Kate Vitasek, Co-Author, Strategic Sourcing in New Economy | Faculty, University of Tennessee
Michele Miller, Vendor Management Office, Black & Veatch
Dharma Ramanathan, VP & Global Head, Telecom, STC Digital
Related Content: Vendor Management
Unlock Ensure Business Alignment in Managed Service Agreements
Get Instant Access
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.
This content is exclusive to members.
Get instant access by signing up!
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.
Search Code: 106716
Last Revised: February 4, 2025
Book an Appointment
IT Research & Advisory Services
Our systems detected an issue with your IP. If you think this is an error please submit your concerns via our contact form.

 Looking at Risk in a New Light: The Six Pillars of Vendor Risk Management
Looking at Risk in a New Light: The Six Pillars of Vendor Risk Management
 Manage Exponential Value Relationships
Manage Exponential Value Relationships
 Jump Start Your Vendor Management Initiative
Jump Start Your Vendor Management Initiative
 Capture and Market the ROI of Your VMO
Capture and Market the ROI of Your VMO
 Cut Cost Through Effective IT Category Planning
Cut Cost Through Effective IT Category Planning
 Design and Build an Effective Contract Lifecycle Management Process
Design and Build an Effective Contract Lifecycle Management Process
 Maximize Value From Your Value-Added Reseller (VAR)
Maximize Value From Your Value-Added Reseller (VAR)
 Drive Successful Sourcing Outcomes With a Robust RFP Process
Drive Successful Sourcing Outcomes With a Robust RFP Process
 Reduce Risk With Rock-Solid Service-Level Agreements
Reduce Risk With Rock-Solid Service-Level Agreements
 Slash Spending by Optimizing Your Software Maintenance and Support
Slash Spending by Optimizing Your Software Maintenance and Support
 Identify and Manage Financial Risk Impacts on Your Organization
Identify and Manage Financial Risk Impacts on Your Organization
 Identify and Manage Strategic Risk Impacts on Your Organization
Identify and Manage Strategic Risk Impacts on Your Organization
 Identify and Manage Reputational Risk Impacts on Your Organization
Identify and Manage Reputational Risk Impacts on Your Organization
 Identify and Manage Security Risk Impacts on Your Organization
Identify and Manage Security Risk Impacts on Your Organization
 Evaluate Your Vendor Account Team to Optimize Vendor Relations
Evaluate Your Vendor Account Team to Optimize Vendor Relations
 Elevate Your Vendor Management Initiative
Elevate Your Vendor Management Initiative
 Prepare for Negotiations More Effectively
Prepare for Negotiations More Effectively
 Implement Your Negotiation Strategy More Effectively
Implement Your Negotiation Strategy More Effectively
 Evaluate and Learn From Your Negotiation Sessions More Effectively
Evaluate and Learn From Your Negotiation Sessions More Effectively
 Proactively Identify and Mitigate Vendor Risk
Proactively Identify and Mitigate Vendor Risk
 Master the Public Cloud IaaS Acquisition Models
Master the Public Cloud IaaS Acquisition Models
 Essentials of Vendor Management for Small Business
Essentials of Vendor Management for Small Business
 Identify and Manage Regulatory and Compliance Risk Impacts on Your Organization
Identify and Manage Regulatory and Compliance Risk Impacts on Your Organization
 Identify and Manage Operational Risk Impacts on Your Organization
Identify and Manage Operational Risk Impacts on Your Organization
 Don’t Allow Software Licensing to Derail Your M&A
Don’t Allow Software Licensing to Derail Your M&A
 Identify and Reduce Agile Contract Risk
Identify and Reduce Agile Contract Risk
 Improve Your Statements of Work to Hold Your Vendors Accountable
Improve Your Statements of Work to Hold Your Vendors Accountable
 Understand Common IT Contract Provisions to Negotiate More Effectively
Understand Common IT Contract Provisions to Negotiate More Effectively
 Master Contract Review and Negotiation for Software Agreements
Master Contract Review and Negotiation for Software Agreements
 Master the MSA for Your Managed Services Providers
Master the MSA for Your Managed Services Providers
 Negotiate SaaS Agreements That Are Built to Last
Negotiate SaaS Agreements That Are Built to Last
 Establish a Vendor Management Roadmap to Succeed With Autonomous Technologies
Establish a Vendor Management Roadmap to Succeed With Autonomous Technologies
 Price Benchmarking & Negotiation
Price Benchmarking & Negotiation
 Stop Wasting Time Evaluating Commoditized Products and Services
Stop Wasting Time Evaluating Commoditized Products and Services
 Ensure Business Alignment in Managed Service Agreements
Ensure Business Alignment in Managed Service Agreements




